Perforin is a critical physiologic regulator of T-cell activation
- PMID: 21606480
- PMCID: PMC3142903
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-324533
Perforin is a critical physiologic regulator of T-cell activation
Abstract
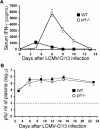
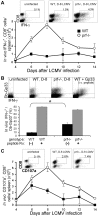
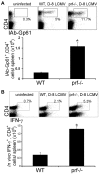
Individuals with impaired perforin-dependent cytotoxic function (Ctx(-)) develop a fatal inflammatory disorder called hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). It has been hypothesized that immune hyperactivation during HLH is caused by heightened infection, defective apoptosis/responsiveness of Ctx(-) lymphocytes, or enhanced antigen presentation. Whereas clinical and experimental data suggest that increased T-cell activation drives HLH, potential abnormalities of T-cell activation have not been well characterized in Ctx(-) hosts. To define such abnormalities and to test these hypotheses, we assessed in vivo T-cell activation kinetics and viral loads after lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection of Ctx(-) mice. We found that increased T-cell activation occurred early during infection of Ctx(-) mice, while they had viral burdens that were identical to those of WT animals, demonstrating that T-cell hyperactivation was independent of viral load. Furthermore, cell transfer and signaling studies indicated that increased antigenic stimulation, not a cell-intrinsic defect of responsiveness, underlay heightened T-cell activation in vivo. Finally, direct measurement of viral antigen presentation demonstrated an increase in Ctx(-) mice that was proportional to abnormal T-cell activation. We conclude that perforin-dependent cytotoxicity has an immunoregulatory role that is distinguishable from its pathogen clearance function and limits T-cell activation in the physiologic context by suppressing antigen presentation.
Figures



References
-
- Filipovich AH. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and related disorders. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;6(6):410–415. - PubMed
-
- Favara BE, Feller AC, Pauli M, et al. Contemporary classification of histiocytic disorders. The WHO Committee On Histiocytic/Reticulum Cell Proliferations. Reclassification Working Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;29(3):157–166. - PubMed
-
- Stepp SE, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Le Deist F, et al. Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science. 1999;286(5446):1957–1959. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI. Biology and treatment of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: importance of perforin in lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and triggering of apoptosis. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002;38(5):305–309. - PubMed
-
- Fadeel B, Orrenius S, Henter JI. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: too little cell death can seriously damage your health. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;42(1–2):13–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

