Adiponectin suppresses gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse hepatocytes independent of LKB1-AMPK signaling
- PMID: 21606593
- PMCID: PMC3104763
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI45942
Adiponectin suppresses gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse hepatocytes independent of LKB1-AMPK signaling
Abstract
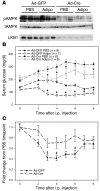
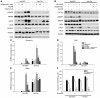
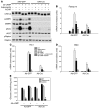
The adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin signals from the fat storage depot to regulate metabolism in peripheral tissues. Inversely correlated with body fat levels, adiponectin reduction in obese individuals may play a causal role in the symptoms of metabolic syndrome. Adiponectin lowers serum glucose through suppression of hepatic glucose production, an effect attributed to activation of AMPK. Here, we investigated the signaling pathways that mediate the effects of adiponectin by studying mice with inducible hepatic deletion of LKB1, an upstream regulator of AMPK. We found that loss of LKB1 in the liver partially impaired the ability of adiponectin to lower serum glucose, though other actions of the hormone were preserved, including reduction of gluconeogenic gene expression and hepatic glucose production as assessed by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. Furthermore, in primary mouse hepatocytes, the absence of LKB1, AMPK, or the transcriptional coactivator CRTC2 did not prevent adiponectin from inhibiting glucose output or reducing gluconeogenic gene expression. These results reveal that whereas some of the hormone's actions in vivo may be LKB1 dependent, substantial LKB1-, AMPK-, and CRTC2-independent signaling pathways also mediate effects of adiponectin.
Figures

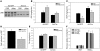

References
-
- Hotta K, et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(6):1595–1599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

