PG F(2α) Receptor: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 21607067
- PMCID: PMC3095374
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2010.00116
PG F(2α) Receptor: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
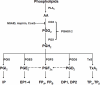
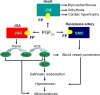
Prostaglandins (PGs), a group of key lipid mediators, are involved in numerous physiological and pathological processes including inflammation and cardiovascular homeostasis. Each PG acts on its specific and distinct cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) or peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). Prostaglandin F(2α) receptor (FP) is required for female reproductive function such as luteolysis and parturition. It has recently been implicated in blood pressure regulation, atherosclerosis and other inflammation-related disorders. The emerging role of FP in cardiovascular diseases is highlighted and potential therapeutic translation is discussed in the current review.
Keywords: FP receptor; atherosclerosis; hypertension; prostaglandin F2alpha.
Figures
References
-
- Abramovitz M., Boie Y., Nguyen T., Rushmore T. H., Bayne M. A., Metters K. M., Slipetz D. M., Grygorczyk R. (1994). Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostanoid FP receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 2632–2636 - PubMed
-
- Adams J. W., Migita D. S., Yu M. K., Young R., Hellickson M. S., Castro-Vargas F. E., Domingo J. D., Lee P. H., Bui J. S., Henderson S. A. (1996). Prostaglandin F2 alpha stimulates hypertrophic growth of cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 1179–1186 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1179 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anthony T. L., Pierce K. L., Stamer W. D., Regan J. W. (1998). Prostaglandin F2 alpha receptors in the human trabecular meshwork. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 39, 315–321 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

