Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of calcium-binding protein 1 in a Ca(2+) -bound closed state: implications for target recognition
- PMID: 21608059
- PMCID: PMC3189521
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.662
Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of calcium-binding protein 1 in a Ca(2+) -bound closed state: implications for target recognition
Abstract
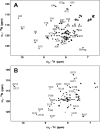
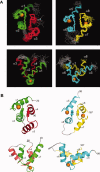
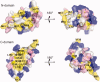
Calcium-binding protein 1 (CaBP1), a neuron-specific member of the calmodulin (CaM) superfamily, regulates the Ca(2+) -dependent activity of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors (InsP3Rs) and various voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels. Here, we present the NMR structure of full-length CaBP1 with Ca(2+) bound at the first, third, and fourth EF-hands. A total of 1250 nuclear Overhauser effect distance measurements and 70 residual dipolar coupling restraints define the overall main chain structure with a root-mean-squared deviation of 0.54 Å (N-domain) and 0.48 Å (C-domain). The first 18 residues from the N-terminus in CaBP1 (located upstream of the first EF-hand) are structurally disordered and solvent exposed. The Ca(2+) -saturated CaBP1 structure contains two independent domains separated by a flexible central linker similar to that in calmodulin and troponin C. The N-domain structure of CaBP1 contains two EF-hands (EF1 and EF2), both in a closed conformation [interhelical angles = 129° (EF1) and 142° (EF2)]. The C-domain contains EF3 and EF4 in the familiar Ca(2+) -bound open conformation [interhelical angles = 105° (EF3) and 91° (EF4)]. Surprisingly, the N-domain adopts the same closed conformation in the presence or absence of Ca(2+) bound at EF1. The Ca(2+) -bound closed conformation of EF1 is reminiscent of Ca(2+) -bound EF-hands in a closed conformation found in cardiac troponin C and calpain. We propose that the Ca(2+) -bound closed conformation of EF1 in CaBP1 might undergo an induced-fit opening only in the presence of a specific target protein, and thus may help explain the highly specialized target binding by CaBP1.
Copyright © 2011 The Protein Society.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett MK. Ca2+ and the regulation of neurotransmitter secretion. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997;7:316–322. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne RD, Morgan A. Ca2+ and secretory-vesicle dynamics. Trends Neurosci. 1995;18:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Haeseleer F, Imanishi Y, Sokal I, Filipek S, Palczewski K. Calcium-binding proteins: intracellular sensors from the calmodulin superfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290:615–623. - PubMed
-
- Mikhaylova M, Sharma Y, Reissner C, Nagel F, Aravind P, Rajini B, Smalla KH, Gundelfinger ED, Kreutz MR. Neuronal Ca2+ signaling via caldendrin and calneurons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1763:1229–1237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

