Differential recruitment of methyl CpG-binding domain factors and DNA methyltransferases by the orphan receptor germ cell nuclear factor initiates the repression and silencing of Oct4
- PMID: 21608077
- PMCID: PMC3468724
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.652
Differential recruitment of methyl CpG-binding domain factors and DNA methyltransferases by the orphan receptor germ cell nuclear factor initiates the repression and silencing of Oct4
Abstract
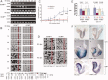
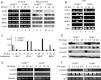
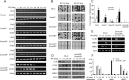
The pluripotency gene Oct4 encodes a key transcription factor that maintains self-renewal of embryonic stem cell (ESC) and is downregulated upon differentiation of ESCs and silenced in somatic cells. A combination of cis elements, transcription factors, and epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation, mediates Oct4 gene expression. Here, we show that the orphan nuclear receptor germ cell nuclear factor (GCNF) initiates Oct4 repression and DNA methylation by the differential recruitment of methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) and DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts) to the Oct4 promoter. When compared with wild-type ESCs and gastrulating embryos, Oct4 repression is lost and its proximal promoter is significantly hypomethylated in retinoic acid (RA)-differentiated GCNF(-/-) ESCs and GCNF(-/-) embryos. Efforts to characterize mediators of GCNF's repressive function and DNA methylation of the Oct4 promoter identified MBD3, MBD2, and de novo Dnmts as GCNF interacting factors. Upon differentiation, endogenous GCNF binds to the Oct4 proximal promoter and differentially recruits MBD3 and MBD2 as well as Dnmt3A. In differentiated GCNF(-/-) ESCs, recruitment of MBD3 and MBD2 as well as Dnmt3A to Oct4 promoter is lost and subsequently Oct4 repression and DNA methylation failed to occur. Hypomethylation of the Oct4 promoter is also observed in RA-differentiated MBD3(-/-) and Dnmt3A(-/-) ESCs, but not in MBD2(-/-) and Dnmt3B(-/-) ESCs. Thus, recruitment of MBD3, MBD2, and Dnmt3A by GCNF links two events: gene-specific repression and DNA methylation, which occur differentially at the Oct4 promoter. GCNF initiates the repression and epigenetic modification of Oct4 gene during ESC differentiation.
Copyright © 2011 AlphaMed Press.
Figures



References
-
- Boiani M, Scholer HR. Regulatory networks in embryo-derived pluripotent stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:872–884. - PubMed
-
- Pan GJ, Chang ZY, Scholer HR, et al. Stem cell pluripotency and transcription factor Oct4. Cell Res. 2002;12:321–329. - PubMed
-
- Chambers I. The molecular basis of pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cloning Stem Cells. 2004;6:386–391. - PubMed
-
- Pesce M, Scholer HR. Oct-4: Control of totipotency and germline determination. Mol Reprod Dev. 2000;55:452–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

