Genome-wide analysis of mobile genetic element insertion sites
- PMID: 21609951
- PMCID: PMC3167599
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr337
Genome-wide analysis of mobile genetic element insertion sites
Abstract
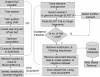
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) account for a significant fraction of eukaryotic genomes and are implicated in altered gene expression and disease. We present an efficient computational protocol for MGE insertion site analysis. ELAN, the suite of tools described here uses standard techniques to identify different MGEs and their distribution on the genome. One component, DNASCANNER analyses known insertion sites of MGEs for the presence of signals that are based on a combination of local physical and chemical properties. ISF (insertion site finder) is a machine-learning tool that incorporates information derived from DNASCANNER. ISF permits classification of a given DNA sequence as a potential insertion site or not, using a support vector machine. We have studied the genomes of Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Drosophila melanogaster and Entamoeba histolytica via a protocol whereby DNASCANNER is used to identify a common set of statistically important signals flanking the insertion sites in the various genomes. These are used in ISF for insertion site prediction, and the current accuracy of the tool is over 65%. We find similar signals at gene boundaries and splice sites. Together, these data are suggestive of a common insertion mechanism that operates in a variety of eukaryotes.
Figures

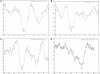
 is defined as the parametric score of substring j (di/trinucleotide) derived from parameter file summed over the m substrings generated for a window of size w.
is defined as the parametric score of substring j (di/trinucleotide) derived from parameter file summed over the m substrings generated for a window of size w.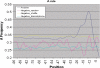




Similar articles
-
An Entamoeba histolytica LINE/SINE pair inserts at common target sites cleaved by the restriction enzyme-like LINE-encoded endonuclease.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Feb;3(1):170-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.1.170-179.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 14871947 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of MGEs and their insertion sites in the gorilla genome.Mob Genet Elements. 2013 Jul 1;3(4):e25675. doi: 10.4161/mge.25675. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Mob Genet Elements. 2013. PMID: 24195013 Free PMC article.
-
Differential distribution of a SINE element in the Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar genomes: role of the LINE-encoded endonuclease.BMC Genomics. 2011 May 25;12:267. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-267. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21612594 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of Dictyostelium discoideum and Entamoeba histolytica.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Oct;8(5):606-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.08.009. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16125444 Review.
-
Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution.Science. 2004 Mar 12;303(5664):1626-32. doi: 10.1126/science.1089670. Science. 2004. PMID: 15016989 Review.
Cited by
-
Detecting motifs and patterns at mobile genetic element insertion site.Bioinformation. 2012;8(16):777-86. doi: 10.6026/97320630008777. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 23055629 Free PMC article.
-
T-lex2: genotyping, frequency estimation and re-annotation of transposable elements using single or pooled next-generation sequencing data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 27;43(4):e22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1250. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25510498 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the application of machine learning in the detection and classification of transposable elements.PeerJ. 2019 Dec 18;7:e8311. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8311. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31976169 Free PMC article.
-
InpactorDB: A Classified Lineage-Level Plant LTR Retrotransposon Reference Library for Free-Alignment Methods Based on Machine Learning.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;12(2):190. doi: 10.3390/genes12020190. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525408 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of MGEs and their insertion sites in the Macaca mulatta genome.Mob Genet Elements. 2012 May 1;2(3):133-141. doi: 10.4161/mge.21074. Mob Genet Elements. 2012. PMID: 23061019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burge C, Karlin S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1997;268:78–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

