The role of Holliday junction resolvases in the repair of spontaneous and induced DNA damage
- PMID: 21609961
- PMCID: PMC3167605
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr277
The role of Holliday junction resolvases in the repair of spontaneous and induced DNA damage
Abstract
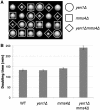
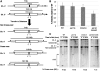
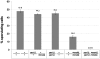
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and other lesions occur frequently during cell growth and in meiosis. These are often repaired by homologous recombination (HR). HR may result in the formation of DNA structures called Holliday junctions (HJs), which need to be resolved to allow chromosome segregation. Whereas HJs are present in most HR events in meiosis, it has been proposed that in vegetative cells most HR events occur through intermediates lacking HJs. A recent screen in yeast has shown HJ resolution activity for a protein called Yen1, in addition to the previously known Mus81/Mms4 complex. Yeast strains deleted for both YEN1 and MMS4 show a reduction in growth rate, and are very sensitive to DNA-damaging agents. In addition, we investigate the genetic interaction of yen1 and mms4 with mutants defective in different repair pathways. We find that in the absence of Yen1 and Mms4 deletion of RAD1 or RAD52 have no further effect, whereas additional sensitivity is seen if RAD51 is deleted. Finally, we show that yeast cells are unable to carry out meiosis in the absence of both resolvases. Our results show that both Yen1 and Mms4/Mus81 play important (although not identical) roles during vegetative growth and in meiosis.
Figures


References
-
- Holliday R. A mechanism for gene conversion in fungi. Genet. Res. 1964;5:283–304. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, West SC. Happy Hollidays: 40th anniversary of the Holliday junction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:937–944. - PubMed
-
- Bergerat A, de Massy B, Gadelle D, Varoutas PC, Nicolas A, Forterre P. An atypical topoisomerase II from Archaea with implications for meiotic recombination. Nature. 1997;386:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

