A novel chemically directed route for the generation of definitive endoderm from human embryonic stem cells based on inhibition of GSK-3
- PMID: 21610099
- PMCID: PMC3104033
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.081679
A novel chemically directed route for the generation of definitive endoderm from human embryonic stem cells based on inhibition of GSK-3
Abstract
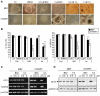
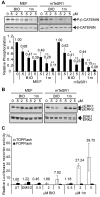
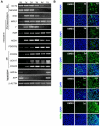
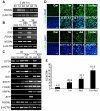
The use of small molecules to 'chemically direct' differentiation represents a powerful approach to promote specification of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) towards particular functional cell types for use in regenerative medicine and pharmaceutical applications. Here, we demonstrate a novel route for chemically directed differentiation of human ESCs (hESCs) into definitive endoderm (DE) exploiting a selective small-molecule inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3). This GSK-3 inhibitor, termed 1m, when used as the only supplement to a chemically defined feeder-free culture system, effectively promoted differentiation of ESC lines towards primitive streak (PS), mesoderm and DE. This contrasts with the role of GSK-3 in murine ESCs, where GSK-3 inhibition promotes pluripotency. Interestingly, 1m-mediated induction of differentiation involved transient NODAL expression and Nodal signalling. Prolonged treatment of hESCs with 1m resulted in the generation of a population of cells displaying hepatoblast characteristics, that is expressing α-fetoprotein and HNF4α. Furthermore, 1m-induced DE had the capacity to mature and generate hepatocyte-like cells capable of producing albumin. These findings describe, for the first time, the utility of GSK-3 inhibition, in a chemically directed approach, to a method of DE generation that is robust, potentially scalable and applicable to different hESC lines.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal S., Holton K. L., Lanza R. (2008). Efficient differentiation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26, 1117-1127 - PubMed
-
- Besser D. (2004). Expression of Nodal, Lefty-A and Left-B in undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells requires activation of Smad2/3. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 45076-45084 - PubMed
-
- Bone H. K., Damiano T., Bartlett S., Perry A., Letchford J., Ripoll Y. S., Nelson A. S., Welham M. J. (2009). Involvement of GSK-3 in regulation of murine embryonic stem cell self-renewal revealed by a series of bisindolylmaleimides. Chem. Biol. 16, 15-27 - PubMed
-
- Brennan J., Lu C., Norris D., Rodriguez T., Beddington R., Robertson E. (2001). Nodal signaling in the epiblast patterns the early mouse embryo. Nature 411, 965-969 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

