Long-term outcome of individuals treated with oral insulin: diabetes prevention trial-type 1 (DPT-1) oral insulin trial
- PMID: 21610124
- PMCID: PMC3120180
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-0523
Long-term outcome of individuals treated with oral insulin: diabetes prevention trial-type 1 (DPT-1) oral insulin trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the long-term intervention effects of oral insulin on the development of type 1 diabetes and to assess the rate of progression to type 1 diabetes before and after oral insulin treatment was stopped in the Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 (DPT-1).
Research design and methods: The follow-up included subjects who participated in the early intervention of oral insulin (1994-2003) to prevent or delay type 1 diabetes. A telephone survey was conducted in 2009 to determine whether diabetes had been diagnosed and, if not, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and autoantibody levels were obtained on all subjects who agreed to participate.
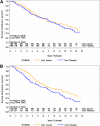
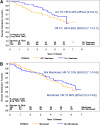
Results: Of 372 subjects randomized, 97 developed type 1 diabetes before follow-up; 75% of the remaining 275 subjects were contacted. In the interim, 77 subjects had been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes and 54 of the remainder have had an OGTT; 10 of these were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, subsequently. Among individuals meeting the original criteria for insulin autoantibodies (IAAs) (≥80 nU/mL), the overall benefit of oral insulin remained significant (P=0.05). However, the hazard rate in this group increased (from 6.4% [95% CI 4.5-9.1] to 10.0% [7.1-14.1]) after cessation of therapy, which approximated the rate of individuals treated with placebo (10.2% [7.1-14.6]).
Conclusions: Overall, the oral insulin treatment effect in individuals with confirmed IAA≥80 nU/mL appeared to be maintained with additional follow-up; however, once therapy stopped, the rate of developing diabetes in the oral insulin group increased to a rate similar to that in the placebo group.
Figures

References
-
- Skyler JS, Krischer JP, Wolfsdorf J, et al. Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes: the Diabetes Prevention Trial–Type 1. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1068–1076 - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Prevention Trial–Type 1 Diabetes Study Group Effects of insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1685–1691 - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Miao D, Babu S, et al. Prevalence of autoantibody-negative diabetes is not rare at all ages and increases with older age and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:88–92 - PubMed
-
- Mahon JL, Sosenko JM, Rafkin-Mervis L, et al. The TrialNet Natural History Study of the Development of Type 1 Diabetes: objectives, design, and initial results. Pediatr Diabetes 2009;10:97–104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

