AGE restriction in diabetes mellitus: a paradigm shift
- PMID: 21610689
- PMCID: PMC3708644
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.74
AGE restriction in diabetes mellitus: a paradigm shift
Abstract
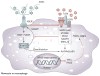
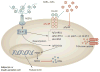
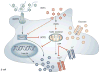
Persistently elevated oxidative stress and inflammation precede or occur during the development of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus and precipitate devastating complications. Given the rapidly increasing incidence of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the space of a few decades, new genetic mutations are unlikely to be the cause, instead pointing to environmental initiators. A hallmark of contemporary culture is a preference for thermally processed foods, replete with pro-oxidant advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). These molecules are appetite-increasing and, thus, efficient enhancers of overnutrition (which promotes obesity) and oxidant overload (which promotes inflammation). Studies of genetic and nongenetic animal models of diabetes mellitus suggest that suppression of host defenses, under sustained pressure from food-derived AGEs, may potentially shift homeostasis towards a higher basal level of oxidative stress, inflammation and injury of both insulin-producing and insulin-responsive cells. This sequence promotes both types of diabetes mellitus. Reducing basal oxidative stress by AGE restriction in mice, without energy or nutrient change, reinstates host defenses, alleviates inflammation, prevents diabetes mellitus, vascular and renal complications and extends normal lifespan. Studies in healthy humans and in those with diabetes mellitus show that consumption of high amounts of food-related AGEs is a determinant of insulin resistance and inflammation and that AGE restriction improves both. This Review focuses on AGEs as novel initiators of oxidative stress that precedes, rather than results from, diabetes mellitus. Therapeutic gains from AGE restriction constitute a paradigm shift.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med. 1997;14 (Suppl 5):S1–S85. - PubMed
-
- Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A, Mohanty P, Garg R. Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation. 2005;111:1448–1454. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES. Risks for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes associated with the metabolic syndrome: a summary of the evidence. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1769–1778. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, et al. Trends in the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus from the 1970s to the 1990s: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2006;113:2914–2918. - PubMed
-
- Harjutsalo V, Sjöberg L, Tuomilehto J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371:1777–1782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

