Short-term plasticity of gray matter associated with leptin deficiency and replacement
- PMID: 21613360
- PMCID: PMC3146795
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-0314
Short-term plasticity of gray matter associated with leptin deficiency and replacement
Erratum in
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Nov;96(11):3576. Dosage error in article text
Abstract
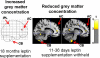
Context: Leptin affects neurogenesis, neuronal growth, and viability. We previously reported that leptin supplementation increased gray matter (GM) concentration in the anterior cingulate gyrus (ACG), cerebellum, and inferior parietal lobule, areas that are also involved in food intake.
Objective: The aim of this study was to report the changes in brain structure at different states of leptin supplementation.
Design: We conducted a nonrandomized trial.
Setting and patients: We studied three adults with congenital leptin deficiency due to a mutation in the leptin gene.
Intervention: Patients received treatment with recombinant methionyl human leptin, with annual 11- to 36-d periods of treatment withholding followed by treatment restoration over 3 yr.
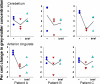
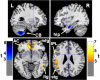
Main outcome measures: GM concentration (by voxel-based morphometry analysis of magnetic resonance scans) was correlated with body mass index (BMI) and leptin supplementation.
Results: Annually withholding leptin supplementation for several weeks increased BMI and reversed the original effects of leptin in the cerebellum and ACG. The changes in the ACG were consistent with an indirect effect of leptin mediated through increased BMI. In the cerebellum, where leptin receptors are most dense, GM changes appeared to be direct effects of leptin. Leptin restoration did not lead to recovery of GM in the short term but did lead to an unexpected GM increase in the posterior half of the left thalamus, particularly the pulvinar nucleus.
Conclusion: These findings provide the first in vivo evidence of remarkably plastic, reversible, and regionally specific effects of leptin on human brain morphology. They suggest that leptin may have therapeutic value in modulating plasticity-dependent brain functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of leptin deficiency and replacement on cerebellar response to food-related cues.Cerebellum. 2013 Feb;12(1):59-67. doi: 10.1007/s12311-012-0360-z. Cerebellum. 2013. PMID: 22576622 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of leptin replacement on brain structure in genetically leptin-deficient adults.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 May;90(5):2851-4. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1979. Epub 2005 Feb 15. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 15713712
-
Relationships between plasma leptin concentrations and human brain structure: a voxel-based morphometric study.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Feb 2;412(3):248-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.11.019. Epub 2006 Nov 22. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17123711 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Leptin Replacement on Neural Plasticity.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:8528934. doi: 10.1155/2016/8528934. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26881138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortical and subcortical gray matter shrinkage in alcohol-use disorders: a voxel-based meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Jul;66:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.034. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27108216 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated gray matter volume of the emotional cerebellum in women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder.J Affect Disord. 2013 Apr 5;146(2):266-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.06.038. Epub 2012 Aug 4. J Affect Disord. 2013. PMID: 22868063 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of leptin deficiency and replacement on cerebellar response to food-related cues.Cerebellum. 2013 Feb;12(1):59-67. doi: 10.1007/s12311-012-0360-z. Cerebellum. 2013. PMID: 22576622 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis.Front Neurosci. 2013 Apr 8;7:51. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00051. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23579596 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin therapy alters appetite and neural responses to food stimuli in brain areas of leptin-sensitive subjects without altering brain structure.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Dec;99(12):E2529-38. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-2774. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25279500 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology of leptin: energy homeostasis, neuroendocrine function and metabolism.Metabolism. 2015 Jan;64(1):24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Metabolism. 2015. PMID: 25199978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F. 1995. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 269:540–543 - PubMed
-
- Ozata M, Ozdemir IC, Licinio J. 1999. Human leptin deficiency caused by a missense mutation: multiple endocrine defects, decreased sympathetic tone, and immune system dysfunction indicate new targets for leptin action, greater central than peripheral resistance to the effects of leptin, and spontaneous correction of leptin-mediated defects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:3686–3695 - PubMed
-
- Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. 2009. Leptin: a pivotal regulator of human energy homeostasis. Am J Clin Nutr 89:980S–984S - PubMed
-
- Licinio J, Caglayan S, Ozata M, Yildiz BO, de Miranda PB, O'Kirwan F, Whitby R, Liang L, Cohen P, Bhasin S, Krauss RM, Veldhuis JD, Wagner AJ, DePaoli AM, McCann SM, Wong ML. 2004. Phenotypic effects of leptin replacement on morbid obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypogonadism, and behavior in leptin-deficient adults. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4531–4536 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Bjorbaek C, Osei S, Flier JS. 1999. Regulation of neuronal and glial proteins by leptin: implications for brain development. Endocrinology 140:2755–2762 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA020726/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK063240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 DA022539/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01GM061394/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR017365/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20DA022539/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24RR016996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24RR017365/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061394/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR016996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058851/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK058851/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA020726/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States

