High dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy quality assurance: a practical guide
- PMID: 21614233
- PMCID: PMC3097611
- DOI: 10.2349/biij.2.2.e34
High dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy quality assurance: a practical guide
Abstract
The widespread adoption of high dose rate brachytherapy with its inherent dangers necessitates adoption of appropriate quality assurance measures to minimize risks to both patients and medical staff. This paper is aimed at assisting someone who is establishing a new program or revising one already in place into adhere to the recently issued Nuclear Regulatory Commission (USA) regulations and the guidelines from the American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Keywords: High dose rate brachytherapy; quality assurance.
Figures




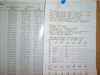

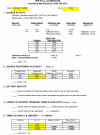


References
-
- Corbett PJ. Brachytherapy in carcinoma of the cervix: The state of the art. In: Martinez AA, Orton CG, Mould RF, editors. Brachytherapy HDR & LDR. Columbia: Nucletron; 1990. pp. 100–9.
-
- U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission [Web Page] Available at http://www.nrc.gov.
-
- Nath R, Anderson LL, Meli JA, et al. Code of practice for brachytherapy physics: report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 56. American Association of Physicists in Medicine. Med Phys. 1997;24(10):1557–98. - PubMed
-
- Kubo HD, Glasgow GP, Pethel TD, et al. High dose-rate brachytherapy treatment delivery: report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 59. Med Phys. 1998;25(4):375–403. - PubMed
-
- Venselaar J, Perez-Calataynd J, editors. A practical guide to quality control of brachytherapy equipment [Web Page] 2004. Available at http://www.estro.be.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
