Host defense pathways: role of redundancy and compensation in infectious disease phenotypes
- PMID: 21616433
- PMCID: PMC3143490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.009
Host defense pathways: role of redundancy and compensation in infectious disease phenotypes
Abstract
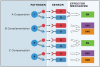
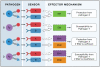
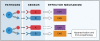
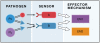
Innate host defense pathways consist of microbial sensors, their signaling pathways, and the antimicrobial effector mechanisms. Several classes of host defense pathways are currently known, each comprising several pattern-recognition receptors that detect different types of pathogens. These pathways interact with one another in a variety of ways that can be categorized into cooperation, complementation, and compensation. Understanding the principles of these interactions is important for better understanding of host defense mechanisms, as well as for correct interpretation of immunodeficient phenotypes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arkwright PD, Abinun M, Cant AJ. Autoimmunity in human primary immunodeficiency diseases. Blood. 2002;99:2694–2702. - PubMed
-
- Elomaa O, Kangas M, Sahlberg C, Tuukkanen J, Sormunen R, Liakka A, Thesleff I, Kraal G, Tryggvason K. Cloning of a novel bacteria-binding receptor structurally related to scavenger receptors and expressed in a subset of macrophages. Cell. 1995;80:603–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

