Increased very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance
- PMID: 21616678
- PMCID: PMC3163828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.04.007
Increased very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance
Abstract
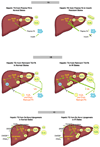
Insulin resistance (IR) affects not only the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism but all aspects of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. IR is associated with increased secretion of VLDL and increased plasma triglycerides, as well as with hepatic steatosis, despite the increased VLDL secretion. Here we link IR with increased VLDL secretion and hepatic steatosis at both the physiologic and molecular levels. Increased VLDL secretion, together with the downstream effects on high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and low density lipoprotein (LDL) size, is proatherogenic. Hepatic steatosis is a risk factor for steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. Understanding the complex inter-relationships between IR and these abnormalities of liver lipid homeostasis will provide insights relevant to new therapies for these increasing clinical problems.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Reaven GM. Why Syndrome X? from Harold Himsworth to the insulin resistance syndrome. Cell Metab. 2005;1:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with Type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–234. - PubMed
-
- Chahil TJ, Ginsberg GN. Diabetic dyslipidemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2006;35:491–510. - PubMed
-
- Barter PJ, Brewer HB, Chapman MJ, Hennekens CH, Rader DJ, Tall AR. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein: a novel target for raising HDL and inhibiting atherosclerosis. Arterio. Thromb. & Vasc. Biol. 2003;23:160–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

