TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis
- PMID: 21617040
- PMCID: PMC3638014
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1204592
TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis
Abstract
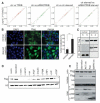
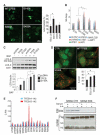
Autophagy is a cellular catabolic process that relies on the cooperation of autophagosomes and lysosomes. During starvation, the cell expands both compartments to enhance degradation processes. We found that starvation activates a transcriptional program that controls major steps of the autophagic pathway, including autophagosome formation, autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and substrate degradation. The transcription factor EB (TFEB), a master gene for lysosomal biogenesis, coordinated this program by driving expression of autophagy and lysosomal genes. Nuclear localization and activity of TFEB were regulated by serine phosphorylation mediated by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2, whose activity was tuned by the levels of extracellular nutrients. Thus, a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism regulates autophagy by controlling the biogenesis and partnership of two distinct cellular organelles.
Figures


Comment in
-
Autophagy: TFEB perfects multitasking.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 8;12(7):404. doi: 10.1038/nrm3139. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21654707 No abstract available.
-
Cell biology. Autophagy's top chef.Science. 2011 Jun 17;332(6036):1392-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1208607. Science. 2011. PMID: 21680833 No abstract available.
-
Transcription factor EB: a central regulator of both the autophagosome and lysosome.Hepatology. 2012 May;55(5):1632-4. doi: 10.1002/hep.25619. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22517549 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

