Do older athletes reach limits in their performance during marathon running?
- PMID: 21617894
- PMCID: PMC3337940
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9271-z
Do older athletes reach limits in their performance during marathon running?
Abstract
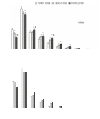
In the last decades, the participation of elderly trained people in endurance events such as marathon running has dramatically increased. Previous studies suggested that the performance of master runners (>40 years) during marathon running has improved. The aims of the study were (1) to analyze the changes in participation and performance trends of master marathon runners between 1980 and 2009, and (2) to compare the gender differences in performance as a function of age across the years. Running times of the best male and female runners between 20 and 79 years of age who competed in the New York City Marathon were analyzed. Gender differences in performance times were analyzed for the top 10 male and female runners between 20 and 65 years of age. The participation of master runners increased during the 1980-2009 period, to a greater extent for females compared to males. During that period, running times of master runners significantly (P < 0.01) decreased for males older than 64 years and for females older than 44 years, respectively. Gender differences in running times decreased over the last three decades but remained relatively stable across the ages during the last decade. These data suggest that male (≥65 years) and female (≥45 years) master runners have probably not yet reached their limits in marathon performance. The relative stability of gender differences in marathon running times across the different age groups over the last decade also suggests that age-related declines in physiological function do not differ between male and female marathoners.
Figures


References
-
- Harper S, Howse K. An upper limit to human longevity? Popul Ageing. 2008;1:99–106. doi: 10.1007/s12062-009-9013-5. - DOI
