Surfactant administration prior to one lung ventilation: physiological and inflammatory correlates in a piglet model
- PMID: 21618717
- PMCID: PMC3320852
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.21485
Surfactant administration prior to one lung ventilation: physiological and inflammatory correlates in a piglet model
Abstract
Objectives: To test the hypothesis that surfactant, when given prophylactically during one lung ventilation (OLV), improves physiological stability and reduces inflammation.
Methods: Prospective controlled animal study. After 30 min of mechanical ventilation, surfactant was administered to the left lung of the treatment group. Right lung mechanical ventilation continued for 3 hr, after which the left lung was unblocked. Bilateral mechanical ventilation was continued for 30 min thereafter. Physiological parameters and biomarkers of inflammation in plasma, lung tissue homogenates, and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) were measured.
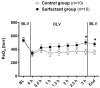
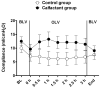
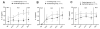
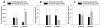
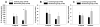
Measurements and main results: Oxygenation improved in the surfactant group, reaching statistical significance at 3 hr of OLV and again after 30 min of bilateral mechanical ventilation following the OLV. Plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-1 β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α showed a trend for reduction. The lung homogenates from the ventilated lungs had significantly lower levels of IL-1 β (P < 0.01) and IL-6 (P < 0.01). The BAL specimen showed an overall reduction in the cytokine levels; IL-1 β was significantly lower in the ventilated lungs (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Surfactant administration improves oxygenation and decreases inflammation, as evidenced by a decrease in several inflammatory cytokines both in the plasma and lungs of a piglet model of OLV.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Jordan S, Mitchell JA, Quinlan GJ, Goldstraw P, Evans TW. The pathogenesis of lung injury following pulmonary resection. Eur Respir J. 2000;15:790–799. - PubMed
-
- Yin K, Gribbin E, Emanuel S, Orndorff R, Walker J, Weese J, Fallahnejad M. Histochemical alterations in one lung ventilation. J Surg Res. 2007;137:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Vanhoutte PM. The endothelium--modulator of vascular smooth-muscle tone. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:512–513. - PubMed
-
- Her C, Mandy S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome of the contralateral lung after reexpansion pulmonary edema of a collapsed lung. J Clin Anesth. 2004;16:244–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

