Effect of concentration on the accuracy of convective imaging distribution of a gadolinium-based surrogate tracer
- PMID: 21619409
- PMCID: PMC4294191
- DOI: 10.3171/2011.3.JNS101381
Effect of concentration on the accuracy of convective imaging distribution of a gadolinium-based surrogate tracer
Abstract
Object: Accurate real-time imaging of coinfused surrogate tracers can be used to determine the convective distribution of therapeutic agents. To assess the effect that a concentration of a Gd-based surrogate tracer has on the accuracy of determining the convective distribution, the authors infused different concentrations of Gd-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) in primates during MR imaging.
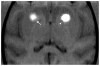
Methods: Five nonhuman primates underwent convective infusion (1 or 5 mM, 21-65 μl) of Gd-DTPA alone, Gd-DTPA and (14)C-sucrose, or Gd-DTPA and (14)C-dextran into the bilateral striata. Animals underwent real-time MR imaging during infusion (5 animals) and autoradiographic analysis (2 animals).
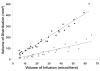
Results: Gadolinium-DTPA could be seen filling the striata at either concentration (1 or 5 mM) on real-time MR imaging. While the volume of distribution (Vd) increased linearly with the volume of infusion (Vi) for both concentrations of tracer (1 mM: R(2) = 0.83; 5 mM: R(2) = 0.96), the Vd/Vi ratio was significantly (p < 0.0001) less for the 1-mM (2.3 ± 1.0) as compared with the 5-mM (7.4 ± 1.9) concentration. Autoradiographic and MR volumetric analysis revealed that the 5-mM concentration most accurately estimated the Vd for both small (sucrose [359 D], 12% difference between imaging and autoradiographic distribution) and large (dextran [70 kD], 0.2% difference) molecules compared with the 1-mM concentration (sucrose, 65% difference; dextran, 68% difference).
Conclusions: The concentration of infused Gd-DTPA plays a critical role in accurately assessing the distribution of molecules delivered by CED. A 5-mM concentration of Gd-DTPA most accurately estimated the Vd over a wide range of molecular sizes.
Figures
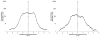
Comment in
-
Convection-enhanced delivery.J Neurosurg. 2011 Sep;115(3):463-4; discussion 465-6. doi: 10.3171/2010.11.JNS101801. Epub 2011 May 27. J Neurosurg. 2011. PMID: 21619413 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bankiewicz KS, Eberling JL, Kohutnicka M, Jagust W, Pivirotto P, Bringas J, et al. Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vector in parkinsonian monkeys; in vivo detection of gene expression and restoration of dopaminergic function using pro-drug approach. Exp Neurol. 2000;164:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Chen MY, Hoffer A, Morrison PF, Hamilton JF, Hughes J, Schlageter KS, et al. Surface properties, more than size, limiting convective distribution of virus-sized particles and viruses in the central nervous system. J Neurosurg. 2005;103:311–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

