Intercalated disc-associated protein, mXin-alpha, influences surface expression of ITO currents in ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 21622147
- PMCID: PMC3278966
- DOI: 10.2741/e344
Intercalated disc-associated protein, mXin-alpha, influences surface expression of ITO currents in ventricular myocytes
Abstract
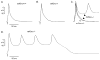
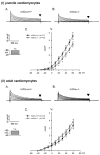
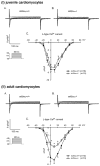
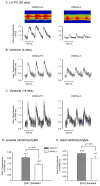
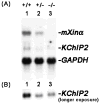
Mouse Xin-alpha (mXin-alpha) encodes a Xin repeat-containing, actin-binding protein localized to the intercalated disc (ICD). Ablation of mXin-alpha progressively leads to disrupted ICD structure, cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy with conduction defects during adulthood. Such conduction defects could be due to ICD structural defects and/or cell electrophysiological property changes. Here, we showed that despite the normal ICD structure, juvenile mXina-null cardiomyocytes (from 3~4-week-old mice) exhibited a significant reduction in the transient outward K+ current (ITO), similar to adult mutant cells. Juvenile but not adult mutant cardiomyocytes also had a significant reduction in the delayed rectifier K+ current. In contrast, the mutant adult ventricular myocytes had a significant reduction in the inward rectifier K+ current (IK1) on hyperpolarization. These together could account for the prolongation of action potential duration (APD) and the ease of developing early afterdepolarization observed in juvenile mXin-alpha-null cells. Interestingly, juvenile mXin-alpha-null cardiomyocytes had a notable decrease in the amplitude of intracellular Ca2+ transient and no change in the L-type Ca2+ current, suggesting that the prolonged APD did not promote an increase in intracellular Ca2+ for cardiac hypertrophy. Juvenile mXin-alpha-null ventricles had reduced levels of membrane-associated Kv channel interacting protein 2, an auxiliary subunit of ITO, and filamin, an actin cross-linking protein. We further showed that mXin-alpha interacted with both proteins, providing a novel mechanism for ITO surface expression.
Figures




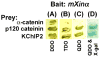

Similar articles
-
Xin proteins and intercalated disc maturation, signaling and diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(7):2566-93. doi: 10.2741/4072. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the roles of Xin repeat-containing proteins in cardiac development, function, and disease.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;310:89-128. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800180-6.00003-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24725425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in ionic currents and reduced conduction velocity in hypertrophied ventricular myocardium of Xin alpha-deficient mice.Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2007 Jul;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):90-2. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2007. PMID: 17584692 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulation of KCNE2 expression modulates action potential duration and Ito and IK in rat and mouse ventricular myocytes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Oct;309(8):H1288-302. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00757.2014. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26297229
-
Elimination of the transient outward current and action potential prolongation in mouse atrial myocytes expressing a dominant negative Kv4 alpha subunit.J Physiol. 1999 Aug 15;519 Pt 1(Pt 1):11-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0011o.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10432335 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Cardiac Hypertrophic Growth in MYBPC3-Null Mice Suggests Early Responders in Hypertrophic Remodeling.Front Physiol. 2018 Oct 25;9:1442. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01442. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30410445 Free PMC article.
-
Xin proteins and intercalated disc maturation, signaling and diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(7):2566-93. doi: 10.2741/4072. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Filamin C: a novel component of the KCNE2 interactome during hypoxia.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016 Jan-Feb;27(1):4-11. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2015-049. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016. PMID: 26956495 Free PMC article.
-
Intercalated disc protein, mXinα, suppresses p120-catenin-induced branching phenotype via its interactions with p120-catenin and cortactin.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Jul 1;535(1):91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.12.018. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23296090 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the roles of Xin repeat-containing proteins in cardiac development, function, and disease.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;310:89-128. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800180-6.00003-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24725425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang DZ, Reiter RS, Lin JL, Wang Q, Williams HS, Krob SL, Schultheiss TM, Evans S, Lin JJ. Requirement of a novel gene, Xin, in cardiac morphogenesis. Development. 1999;126(6):1281–94. - PubMed
-
- Huang HT, Brand OM, Mathew M, Ignatiou C, Ewen EP, McCalmon SA, Naya FJ. Myomaxin is a novel transcriptional target of MEF2A that encodes a Xin-related alpha-actinin-interacting protein. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(51):39370–9. - PubMed
-
- Sinn HW, Balsamo J, Lilien J, Lin JJ. Localization of the novel Xin protein to the adherens junction complex in cardiac and skeletal muscle during development. Dev Dyn. 2002;225(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Gustafson-Wagner EA, Sinn HW, Chen YL, Wang DZ, Reiter RS, Lin JL, Yang B, Williamson RA, Chen J, Lin CI, Lin JJ. Loss of mXinα, an intercalated disk protein, results in cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy with conduction defects. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293(5):H2680–92. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

