G protein-coupled receptor kinases in normal and failing myocardium
- PMID: 21622221
- PMCID: PMC4149910
- DOI: 10.2741/3898
G protein-coupled receptor kinases in normal and failing myocardium
Abstract
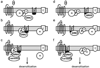
Heart failure (HF) is the end stage of many underlying cardiovascular diseases and is among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in industrialized countries. One of the striking characteristics of HF is the desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling, particularly the beta-adrenergic receptor (betaAR) system. GPCR desensitization is initiated by phosphorylation by GPCR kinases (GRKs), followed by downregulation and functional uncoupling from their G proteins. In the heart, the major GRK isoforms, GRK2 and GRK5, undergo upregulation due to the heightened sympathetic nervous system activity that is characteristic of HF as catecholamine levels increase in an effort to drive the failing pump. This desensitization leads to the distinctive loss of inotropic reserve and functional capacity of the failing heart. Moreover, GRK2 and GRK5 have an increasing non-GPCR interactome, which may play critical roles in cardiac physiology. In the current review, the canonical GPCR kinase function of GRKs and the novel non-GPCR kinase activity of GRKs, their contribution to the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy and HF, and the possibility of GRKs serving as future drug targets will be discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Writing Group M, Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, Gillespie C, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho PM, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott MM, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Roger VL, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J on behalf of the American Heart Association Statistics and S. Stroke Statistics. Executive Summary: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2010 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:948–954. - PubMed
-
- Akhter SA, Luttrell LM, Rockman HA, Iaccarino G, Lefkowitz RJ, Koch WJ. Targeting the receptor-Gq interface to inhibit in vivo pressure overload myocardial hypertrophy. Science. 1998;280:574–577. - PubMed
-
- Heineke J, Molkentin JD. Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Molkentin JD, Dorn GW., 2nd Cytoplasmic signaling pathways that regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:391–426. - PubMed
-
- Pitcher JA, Freedman NJ, Lefkowitz RJ. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:653–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

