How I treat mucormycosis
- PMID: 21622653
- PMCID: PMC3292433
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-316430
How I treat mucormycosis
Abstract
Unlike invasive aspergillosis, the prognosis and outcome of hematologic malignancy patients who develop invasive mucormycosis have not significantly improved over the past decade as a majority of patients who develop the infection still die 12 weeks after diagnosis. However, early recognition and treatment of invasive mucormycosis syndromes, as well as individualized approaches to treatment and secondary prophylaxis, could improve the odds of survival, even in the most persistently immunosuppressed patient receiving chemotherapy and/or of stem cell transplantation. Herein, we describe the subtle clinical and radiographic clues that should alert the hematologist to the possibility of mucormycosis, and aggressive and timely treatment approaches that may limit the spread of infection before it becomes fatal. Hematology patients with this opportunistic infection require integrated care across several disciplines and frequently highly individualized and complex sequence of decision-making. We also offer perspectives for the use of 2 antifungals, amphotericin B products and posaconazole, with activity against Mucorales. The availability of posaconazole in an oral formulation that can be administered safely for prolonged periods makes it an attractive agent for long-term primary and secondary prophylaxis. However, serum drug concentration monitoring may be required to minimize breakthrough infection or relapsing mucormycosis associated with inadequate blood concentrations.
Figures


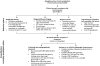
References
-
- Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41(5):634–53. - PubMed
-
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE. Invasive zygomycosis: update on pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2006;20(3):581–607. - PubMed
-
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lewis RE. Agents of mucormycosis and related species. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. Vol 2. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2005. p. 2973.
-
- Kontoyiannis DP, Lionakis MS, Lewis RE, et al. Zygomycosis in a tertiary-care cancer center in the era of Aspergillus-active antifungal therapy: a case-control observational study of 27 recent cases. J Infect Dis. 2005;191(8):1350–1360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

