Group X secretory phospholipase A2 enhances TLR4 signaling in macrophages
- PMID: 21622863
- PMCID: PMC3119755
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003552
Group X secretory phospholipase A2 enhances TLR4 signaling in macrophages
Abstract
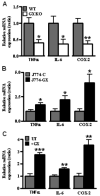
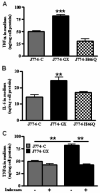
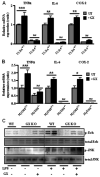
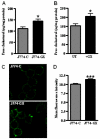
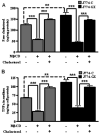
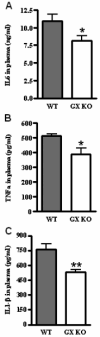
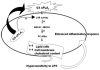
Secretory phospholipase A(2)s (sPLA(2)) hydrolyze glycerophospholipids to liberate lysophospholipids and free fatty acids. Although group X (GX) sPLA(2) is recognized as the most potent mammalian sPLA(2) in vitro, its precise physiological function(s) remains unclear. We recently reported that GX sPLA(2) suppresses activation of the liver X receptor in macrophages, resulting in reduced expression of liver X receptor-responsive genes including ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 (ABCA1) and G1 (ABCG1), and a consequent decrease in cellular cholesterol efflux and increase in cellular cholesterol content (Shridas et al. 2010. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30: 2014-2021). In this study, we provide evidence that GX sPLA(2) modulates macrophage inflammatory responses by altering cellular cholesterol homeostasis. Transgenic expression or exogenous addition of GX sPLA(2) resulted in a significantly higher induction of TNF-α, IL-6, and cyclooxygenase-2 in J774 macrophage-like cells in response to LPS. This effect required GX sPLA(2) catalytic activity, and was abolished in macrophages that lack either TLR4 or MyD88. The hypersensitivity to LPS in cells overexpressing GX sPLA(2) was reversed when cellular free cholesterol was normalized using cyclodextrin. Consistent with results from gain-of-function studies, peritoneal macrophages from GX sPLA(2)-deficient mice exhibited a significantly dampened response to LPS. Plasma concentrations of inflammatory cytokines were significantly lower in GX sPLA(2)-deficient mice compared with wild-type mice after LPS administration. Thus, GX sPLA(2) amplifies signaling through TLR4 by a mechanism that is dependent on its catalytic activity. Our data indicate this effect is mediated through alterations in plasma membrane free cholesterol and lipid raft content.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Group X secretory phospholipase A2 negatively regulates ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression and cholesterol efflux in macrophages.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Oct;30(10):2014-21. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.210237. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20844270 Free PMC article.
-
Group X secretory phospholipase A2 regulates the expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) in mouse adrenal glands.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):20031-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090423. Epub 2010 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20421306 Free PMC article.
-
Increased inflammatory gene expression in ABC transporter-deficient macrophages: free cholesterol accumulation, increased signaling via toll-like receptors, and neutrophil infiltration of atherosclerotic lesions.Circulation. 2008 Oct 28;118(18):1837-47. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.793869. Epub 2008 Oct 13. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18852364 Free PMC article.
-
Role of secretory phospholipase a(2) in CNS inflammation: implications in traumatic spinal cord injury.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Jun;7(3):254-69. doi: 10.2174/187152708784936671. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18673210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular lipid flux and membrane microdomains as organizing principles in inflammatory cell signaling.J Immunol. 2011 Aug 15;187(4):1529-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100253. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21810617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)-an emerging therapeutic target for persistent pain states.Pain. 2018 Oct;159(10):1908-1915. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001306. Pain. 2018. PMID: 29889119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergy between 15-lipoxygenase and secreted PLA2 promotes inflammation by formation of TLR4 agonists from extracellular vesicles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 13;117(41):25679-25689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005111117. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32973091 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of the Secreted Phospholipase A2 Gene Family in Immunology.Adv Immunol. 2016;132:91-134. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Adv Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27769509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Old but New: Group IIA Phospholipase A2 as a Modulator of Gut Microbiota.Metabolites. 2022 Apr 14;12(4):352. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040352. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35448539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoquality control by phospholipase A2 enzymes.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017;93(9):677-702. doi: 10.2183/pjab.93.043. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29129849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: The road ahead. Cell. 2001;104:503–516. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Schwabe RF, DeVries-Seimon T, Yao PM, Gerbod-Giannone MC, Tall AR, Davis RJ, Flavell R, Brenner DA, Tabas I. Free cholesterol-loaded macrophages are an abundant source of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6: model of NF-kappaB- and map kinase-dependent inflammation in advanced atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:21763–21772. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Lee JY, Timmins JM, Brown JM, Boudyguina E, Mulya A, Gebre AK, Willingham MC, Hiltbold EM, Mishra N, Maeda N, Parks JS. Increased cellular free cholesterol in macrophage-specific Abca1 knock-out mice enhances pro-inflammatory response of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:22930–22941. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

