Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes Th17 allergic asthma in mice
- PMID: 21622869
- PMCID: PMC3119761
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100500
Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes Th17 allergic asthma in mice
Abstract
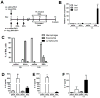
IL-1β is a cytokine critical to several inflammatory diseases in which pathogenic Th17 responses are implicated. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by microbial and environmental stimuli can enable the caspase-1-dependent processing and secretion of IL-1β. The acute-phase protein serum amyloid A (SAA) is highly induced during inflammatory responses, wherein it participates in systemic modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Elevated levels of IL-1β, SAA, and IL-17 are present in subjects with severe allergic asthma, yet the mechanistic relationship among these mediators has yet to be identified. In this study, we demonstrate that Saa3 is expressed in the lungs of mice exposed to several mixed Th2/Th17-polarizing allergic sensitization regimens. SAA instillation into the lungs elicits robust TLR2-, MyD88-, and IL-1-dependent pulmonary neutrophilic inflammation. Furthermore, SAA drives production of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-23, and PGE(2), causes dendritic cell (DC) maturation, and requires TLR2, MyD88, and the NLRP3 inflammasome for secretion of IL-1β by DCs and macrophages. CD4(+) T cells polyclonally stimulated in the presence of conditioned media from SAA-exposed DCs produced IL-17, and the capacity of polyclonally stimulated splenocytes to secrete IL-17 is dependent upon IL-1, TLR2, and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Additionally, in a model of allergic airway inflammation, administration of SAA to the lungs functions as an adjuvant to sensitize mice to inhaled OVA, resulting in leukocyte influx after Ag challenge and a predominance of IL-17 production from restimulated splenocytes that is dependent upon IL-1R signaling.
Figures

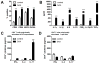



References
-
- Glaccum MB, Stocking KL, Charrier K, Smith JL, Willis CR, Maliszewski C, Livingston DJ, Peschon JJ, Morrissey PJ. Phenotypic and functional characterization of mice that lack the type I receptor for IL-1. J Immunol. 1997;159:3364–3371. - PubMed
-
- Masters SL, Dunne A, Subramanian SL, Hull RL, Tannahill GM, Sharp FA, Becker C, Franchi L, Yoshihara E, Chen Z, Mullooly N, Mielke LA, Harris J, Coll RC, Mills KH, Mok KH, Newsholme P, Nunez G, Yodoi J, Kahn SE, Lavelle EC, O’Neill LA. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by islet amyloid polypeptide provides a mechanism for enhanced IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Nat Immunol. 11:897–904. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Daheshia M, Yao JQ. The interleukin 1beta pathway in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:2306–2312. - PubMed
-
- Clutterbuck AL, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M, Allaway D, Harris P. Interleukin-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degradation and glycosaminoglycan release is inhibited by curcumin in an explant model of cartilage inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1171:428–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

