Distinct functions of kainate receptors in the brain are determined by the auxiliary subunit Neto1
- PMID: 21623363
- PMCID: PMC3125417
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2837
Distinct functions of kainate receptors in the brain are determined by the auxiliary subunit Neto1
Abstract
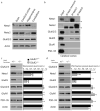
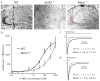
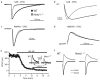
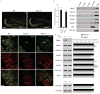
Ionotropic glutamate receptors principally mediate fast excitatory transmission in the brain. Among the three classes of ionotropic glutamate receptors, kainate receptors (KARs) have a unique brain distribution, which has been historically defined by (3)H-radiolabeled kainate binding. Compared with recombinant KARs expressed in heterologous cells, synaptic KARs exhibit characteristically slow rise-time and decay kinetics. However, the mechanisms responsible for these distinct KAR properties remain unclear. We found that both the high-affinity binding pattern in the mouse brain and the channel properties of native KARs are determined by the KAR auxiliary subunit Neto1. Through modulation of agonist binding affinity and off-kinetics of KARs, but not trafficking of KARs, Neto1 determined both the KAR high-affinity binding pattern and the distinctively slow kinetics of postsynaptic KARs. By regulating KAR excitatory postsynaptic current kinetics, Neto1 can control synaptic temporal summation, spike generation and fidelity.
Figures


Comment in
-
Net(o) excitement for kainate receptors.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun 27;14(7):808-10. doi: 10.1038/nn.2864. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21709676 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lerma J. Kainate receptor physiology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Pinheiro PS, Mulle C. Presynaptic glutamate receptors: physiological functions and mechanisms of action. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:423–436. - PubMed
-
- Jane DE, Lodge D, Collingridge GL. Kainate receptors: pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:90–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

