The relation between reproductive value and genetic contribution
- PMID: 21624999
- PMCID: PMC3176105
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.111.127555
The relation between reproductive value and genetic contribution
Abstract
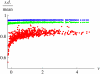
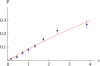
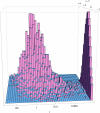
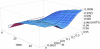
What determines the genetic contribution that an individual makes to future generations? With biparental reproduction, each individual leaves a "pedigree" of descendants, determined by the biparental relationships in the population. The pedigree of an individual constrains the lines of descent of each of its genes. An individual's reproductive value is the expected number of copies of each of its genes that is passed on to distant generations conditional on its pedigree. For the simplest model of biparental reproduction (analogous to the Wright-Fisher model), an individual's reproductive value is determined within ∼10 generations, independent of population size. Partial selfing and subdivision do not greatly slow this convergence. Our central result is that the probability that a gene will survive is proportional to the reproductive value of the individual that carries it and that, conditional on survival, after a few tens of generations, the distribution of the number of surviving copies is the same for all individuals, whatever their reproductive value. These results can be generalized to the joint distribution of surviving blocks of the ancestral genome. Selection on unlinked loci in the genetic background may greatly increase the variance in reproductive value, but the above results nevertheless still hold. The almost linear relationship between survival probability and reproductive value also holds for weakly favored alleles. Thus, the influence of the complex pedigree of descendants on an individual's genetic contribution to the population can be summarized through a single number: its reproductive value.
Figures
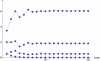
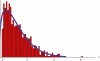
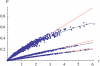
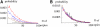


References
-
- Baird S. J. E., Barton N. H., Etheridge A. M., 2003. The distribution of the surviving blocks of an ancestral genome. Theor. Popul. Biol. 64: 451–471 - PubMed
-
- Ballou J. D., 1997. Ancestral inbreeding only minimally affects inbreeding depression in mammalian populations. J. Hered. 88: 169–178 - PubMed
-
- Bulmer M. G., 1971. The effect of selection on genetic variability. Am. Nat. 105: 201–211
-
- Cannings C., Thompson E. A., Skolnick M., 1978. Probability functions on complex pedigrees. Adv. Appl. Probab. 10: 26–61
-
- Caswell H., 1982. Optimal life histories and the maximization of reproductive value: a general theorem for complex life cycles. Ecology 63: 1218–1222
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

