Phytobezoar: an unusual cause of intestinal obstruction
- PMID: 21625276
- PMCID: PMC3097591
- DOI: 10.2349/biij.1.1.e4
Phytobezoar: an unusual cause of intestinal obstruction
Abstract
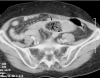
Small bowel phytobezoars are rare and almost always obstructive. There have been previously reported cases of phytobezoars in the literature, however there are few reports on radiological findings for small bowel bezoars. Barium studies characteristically show an intraluminal filling defect of variable size that is not fixed to the bowel wall with barium filling the interstices giving a mottled appearance. On CT scan, the presence of a round or ovoid intraluminal mass with a 'mottled gas' pattern is believed to be pathognomonic. Since features on CT scans are characteristics and physical findings are of little assistance in the diagnosis of bezoar, the diagnostic value of CT needs to be emphasised.
Keywords: Phytobezoars; small bowel obstruction.
Figures


References
-
- Acar T, Tuncal S, Aydin R. An unusual cause of gastrointestinal obstruction: bezoar. N Z Med J. 2003;116(1173):U422. - PubMed
-
- Yildirim T, Yildirim S, Barutcu O, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to phytobezoar: CT diagnosis. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(11):2659–61. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Ha HK, Sohn MJ, et al. CT findings of phytobezoar associated with small bowel obstruction. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(2):299–304. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeropoulou C, Kraniotis P, Zabakis P, et al. Small bowel obstruction due to phytobezoar: CT findings. European Association of Radiology. 2003 Clinical case 2840.
-
- Andrus CH, Ponsky JL. Bezoars: classification, pathophysiology, and treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988;83(5):476–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
