Standard operation procedures for conducting the on-the-road driving test, and measurement of the standard deviation of lateral position (SDLP)
- PMID: 21625472
- PMCID: PMC3100218
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S19639
Standard operation procedures for conducting the on-the-road driving test, and measurement of the standard deviation of lateral position (SDLP)
Abstract
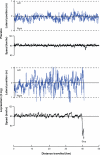
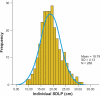
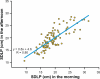
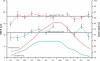
This review discusses the methodology of the standardized on-the-road driving test and standard operation procedures to conduct the test and analyze the data. The on-the-road driving test has proven to be a sensitive and reliable method to examine driving ability after administration of central nervous system (CNS) drugs. The test is performed on a public highway in normal traffic. Subjects are instructed to drive with a steady lateral position and constant speed. Its primary parameter, the standard deviation of lateral position (SDLP), ie, an index of 'weaving', is a stable measure of driving performance with high test-retest reliability. SDLP differences from placebo are dose-dependent, and do not depend on the subject's baseline driving skills (placebo SDLP). It is important that standard operation procedures are applied to conduct the test and analyze the data in order to allow comparisons between studies from different sites.
Keywords: SDLP; driving test; highway; methodology; on-the-road.
Figures








References
-
- Vermeeren A, de Gier JJ, O’Hanlon JF. Methodological guidelines for experimental drugs affecting driving performance: an international expert survey. Maastricht: Institute for Human Psychopharmacology, University of Limburg, The Netherlands; 1993.
-
- O’Hanlon JF, Haak TW, Blaauw GJ, Riemersma JB. Diazepam impairs lateral position control in highway driving. Science. 1982;217(4554):79–81. - PubMed
-
- O’Hanlon JF. Are actual driving tests necessary for evaluating drug safety? Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1988;3(Suppl 1):81–85. - PubMed
-
- Penning R, Veldstra J, Daamen AP, Olivier B, Verster JC. Drugs of abuse, driving and traffic safety. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010;3(1):23–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

