The participation of calponin in the cross talk between 20-hydroxyecdysone and juvenile hormone signaling pathways by phosphorylation variation
- PMID: 21625546
- PMCID: PMC3098250
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019776
The participation of calponin in the cross talk between 20-hydroxyecdysone and juvenile hormone signaling pathways by phosphorylation variation
Abstract
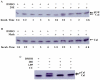
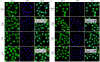
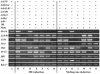
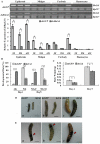
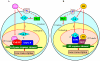
20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) and juvenile hormone (JH) signaling pathways interact to mediate insect development, but the mechanism of this interaction is poorly understood. Here, a calponin homologue domain (Chd) containing protein (HaCal) is reported to play a key role in the cross talk between 20E and JH signaling by varying its phosphorylation. Chd is known as an actin binding domain present in many proteins including some signaling proteins. Using an epidermal cell line (HaEpi), HaCal was found to be up-regulated by either 20E or the JH analog methoprene (JHA). 20E induced rapid phosphorylation of HaCal whereas no phosphorylation occurred with JHA. HaCal could be quickly translocated into the nuclei through 20E or JH signaling but interacted with USP1 only under the mediation of JHA. Knockdown of HaCal by RNAi blocked the 20E inducibility of USP1, PKC and HR3, and also blocked the JHA inducibility of USP1, PKC and JHi. After gene silencing of HaCal by ingestion of dsHaCal expressed by Escherichia coli, the larval development was arrested and the gene expression of USP1, PKC, HR3 and JHi were blocked. These composite data suggest that HaCal plays roles in hormonal signaling by quickly transferring into nucleus to function as a phosphorylated form in the 20E pathway and as a non-phosphorylated form interacting with USP1 in the JH pathway to facilitate 20E or JH signaling cascade, in short, by switching its phosphorylation status to regulate insect development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ozlu N, Akten B, Timm W, Haseley N, Steen H, et al. Phosphoproteomics. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010;2:255–276. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert LI, Granger NA, Roe RM. The juvenile hormones: historical facts and speculations on future research directions. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;30:617–644. - PubMed
-
- Riddiford LM, Hiruma K, Zhou X, Nelson CA. Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;33:1327–1338. - PubMed
-
- Williams CM. The juvenile hormone II. Its role in the endocrine control of molting, pupation, and adult development in the Cecropia silkworm. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1961;16:6–11.
-
- Zhou X, Riddiford LM. Broad specifies pupal development and mediates the 'status quo' action of juvenile hormone on the pupal-adult transformation in Drosophila and Manduca. Development. 2002;129:2259–2269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

