Unraveling the distributed neural code of facial identity through spatiotemporal pattern analysis
- PMID: 21628569
- PMCID: PMC3116398
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1102433108
Unraveling the distributed neural code of facial identity through spatiotemporal pattern analysis
Abstract
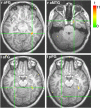
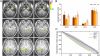
Face individuation is one of the most impressive achievements of our visual system, and yet uncovering the neural mechanisms subserving this feat appears to elude traditional approaches to functional brain data analysis. The present study investigates the neural code of facial identity perception with the aim of ascertaining its distributed nature and informational basis. To this end, we use a sequence of multivariate pattern analyses applied to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. First, we combine information-based brain mapping and dynamic discrimination analysis to locate spatiotemporal patterns that support face classification at the individual level. This analysis reveals a network of fusiform and anterior temporal areas that carry information about facial identity and provides evidence that the fusiform face area responds with distinct patterns of activation to different face identities. Second, we assess the information structure of the network using recursive feature elimination. We find that diagnostic information is distributed evenly among anterior regions of the mapped network and that a right anterior region of the fusiform gyrus plays a central role within the information network mediating face individuation. These findings serve to map out and characterize a cortical system responsible for individuation. More generally, in the context of functionally defined networks, they provide an account of distributed processing grounded in information-based architectures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- DiCarlo JJ, Cox DD. Untangling invariant object recognition. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007;11:333–341. - PubMed
-
- Jiang X, et al. Evaluation of a shape-based model of human face discrimination using FMRI and behavioral techniques. Neuron. 2006;50:159–172. - PubMed
-
- Fairhall SL, Ishai A. Effective connectivity within the distributed cortical network for face perception. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:2400–2406. - PubMed
-
- Gauthier I, et al. The fusiform “face area” is part of a network that processes faces at the individual level. J Cogn Neurosci. 2000;12:495–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

