An integrated health-economic analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in the treatment of moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 21629357
- PMCID: PMC3098944
- DOI: 10.5665/SLEEP.1030
An integrated health-economic analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in the treatment of moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Study objectives: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common disorder associated with substantially increased cardiovascular risks, reduced quality of life, and increased risk of motor vehicle collisions due to daytime sleepiness. This study evaluates the cost-effectiveness of three commonly used diagnostic strategies (full-night polysomnography, split-night polysomnography, unattended portable home-monitoring) in conjunction with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe OSA.
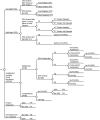
Design: A Markov model was created to compare costs and effectiveness of different diagnostic and therapeutic strategies over a 10-year interval and the expected lifetime of the patient. The primary measure of cost-effectiveness was incremental cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained.
Patients or participants: Baseline computations were performed for a hypothetical average cohort of 50-year-old males with a 50% pretest probability of having moderate-to-severe OSA (apnea-hypopnea index [AHI] ≥ 15 events per hour).
Measurements and results: For a patient with moderate-to-severe OSA, CPAP therapy has an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of $15,915 per QALY gained for the lifetime horizon. Over the lifetime horizon in a population with 50% prevalence of OSA, full-night polysomnography in conjunction with CPAP therapy is the most economically efficient strategy at any willingness-to-pay greater than $17,131 per-QALY gained because it dominates all other strategies in comparative analysis.
Conclusions: Full-night polysomnography (PSG) is cost-effective and is the preferred diagnostic strategy for adults suspected to have moderate-to-severe OSA when all diagnostic options are available. Split-night PSG and unattended home monitoring can be considered cost-effective alternatives when full-night PSG is not available.
Keywords: Markov model; Sleep apnea; comparative effectiveness; continuous positive airway pressure; health-economics; obstructive.
Figures



Comment in
-
The demise of portable monitoring to diagnose OSA? Not so fast!Sleep. 2011 Jun 1;34(6):691-2. doi: 10.5665/SLEEP.1026. Sleep. 2011. PMID: 21629355 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kapur V, Strohl KP, Redline S, Iber C, O'Connor G, Nieto J. Underdiagnosis of sleep apnea syndrome in U.S. communities. Sleep Breath. 2002;6:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Ayas NT, FitzGerald JM, Fleetham JA, et al. Cost-effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure therapy for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:977–84. - PubMed
-
- Weatherly HL, Griffin SC, Mc Daid C, et al. An economic analysis of continuous positive airway pressure for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2009;25:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Sadatsafavi M, Marra CA, Ayas NT, Stradling J, Fleetham J. Cost-effectiveness of oral appliances in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea. Sleep Breath. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Mar J, Rueda JR, Duran-Cantolla J, Schechter C, Chilcott J. The cost-effectiveness of nCPAP treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J. 2003;21:515–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

