Percutaneous treatment of intervertebral disc herniation
- PMID: 21629404
- PMCID: PMC3036519
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1253513
Percutaneous treatment of intervertebral disc herniation
Abstract
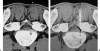
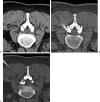
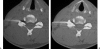
Interventional radiology plays a major role in the management of symptomatic intervertebral disc herniations. In the absence of significant pain relief with conservative treatment including oral pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs, selective image-guided periradicular infiltrations are generally indicated. The precise control of needle positioning allows optimal distribution of steroids along the painful nerve root. After 6 weeks of failure of conservative treatment including periradicular infiltration, treatment aiming to decompress or remove the herniation is considered. Conventional open surgery offers suboptimal results and is associated with significant morbidity. To achieve minimally invasive discal decompression, different percutaneous techniques have been developed. Their principle is to remove a small volume of nucleus, which results in an important reduction of intradiscal pressure and subsequently reduction of pressure inside the disc herniation. However, only contained disc herniations determined by computed tomography or magnetic resonance are indicated for these techniques. Thermal techniques such as radiofrequency or laser nucleotomy seem to be more effective than purely mechanical nucleotomy; indeed, they achieve discal decompression but also thermal destruction of intradiscal nociceptors, which may play a major role in the physiopathology of discal pain. The techniques of image-guided spinal periradicular infiltration and percutaneous nucleotomy with laser and radiofrequency are presented with emphasis on their best indications.
Keywords: Disc herniation; laser; percutaneous nucleotomy; periradicular infiltration; radiofrequency.
Figures








References
-
- Castro I, Santos D P, Christoph DdeH, Landeiro J A. The history of spinal surgery for disc disease: an illustrated timeline. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005;63(3A):701–706. - PubMed
-
- Burke J G, Watson R W, McCormack D, Dowling F E, Walsh M G, Fitzpatrick J M. Intervertebral discs which cause low back pain secrete high levels of proinflammatory mediators. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Coppes M H, Marani E, Thomeer R T, Groen G J. Innervation of “painful” lumbar discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:2342–2349. discussion 2349–2350. - PubMed
-
- Smith L, Garvin P J, Gesler R M, Jennings R B. Enzyme dissolution of the nucleus pulposus. Nature. 1963;198:1311–1312. - PubMed

