gp100 peptide vaccine and interleukin-2 in patients with advanced melanoma
- PMID: 21631324
- PMCID: PMC3517182
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1012863
gp100 peptide vaccine and interleukin-2 in patients with advanced melanoma
Abstract
Background: Stimulating an immune response against cancer with the use of vaccines remains a challenge. We hypothesized that combining a melanoma vaccine with interleukin-2, an immune activating agent, could improve outcomes. In a previous phase 2 study, patients with metastatic melanoma receiving high-dose interleukin-2 plus the gp100:209-217(210M) peptide vaccine had a higher rate of response than the rate that is expected among patients who are treated with interleukin-2 alone.
Methods: We conducted a randomized, phase 3 trial involving 185 patients at 21 centers. Eligibility criteria included stage IV or locally advanced stage III cutaneous melanoma, expression of HLA*A0201, an absence of brain metastases, and suitability for high-dose interleukin-2 therapy. Patients were randomly assigned to receive interleukin-2 alone (720,000 IU per kilogram of body weight per dose) or gp100:209-217(210M) plus incomplete Freund's adjuvant (Montanide ISA-51) once per cycle, followed by interleukin-2. The primary end point was clinical response. Secondary end points included toxic effects and progression-free survival.
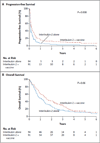
Results: The treatment groups were well balanced with respect to baseline characteristics and received a similar amount of interleukin-2 per cycle. The toxic effects were consistent with those expected with interleukin-2 therapy. The vaccine-interleukin-2 group, as compared with the interleukin-2-only group, had a significant improvement in centrally verified overall clinical response (16% vs. 6%, P=0.03), as well as longer progression-free survival (2.2 months; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.7 to 3.9 vs. 1.6 months; 95% CI, 1.5 to 1.8; P=0.008). The median overall survival was also longer in the vaccine-interleukin-2 group than in the interleukin-2-only group (17.8 months; 95% CI, 11.9 to 25.8 vs. 11.1 months; 95% CI, 8.7 to 16.3; P=0.06).
Conclusions: In patients with advanced melanoma, the response rate was higher and progression-free survival longer with vaccine and interleukin-2 than with interleukin-2 alone. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00019682.).
Figures
Comment in
-
gp100 peptide vaccine in melanoma.N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug 25;365(8):771; author reply 771. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1107536. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21864189 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:411–422. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
