Early clinical development of ARQ 197, a selective, non-ATP-competitive inhibitor targeting MET tyrosine kinase for the treatment of advanced cancers
- PMID: 21632449
- PMCID: PMC3228218
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0380
Early clinical development of ARQ 197, a selective, non-ATP-competitive inhibitor targeting MET tyrosine kinase for the treatment of advanced cancers
Abstract
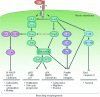
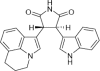
Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase c-MET (MET, mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor) in many cancers, and its participation in multiple signal transduction pathways involved in malignant tumor growth, suggest a wide therapeutic potential for MET inhibition in human cancer. Here we describe the discovery and early clinical development of ARQ 197, a novel, selective, non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of MET. Phase I studies demonstrate that ARQ 197 has a predictable pharmacokinetics and favorable safety profile, making it a potentially ideal partner for combination with cytotoxic chemotherapies and targeted anticancer agents. Results from phase I and phase II trials demonstrate preliminary evidence of anticancer activity. New data from a global phase II randomized trial comparing a combination of ARQ 197 plus erlotinib with erlotinib/placebo, in endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor-naïve patients with locally advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, demonstrate improvement in progression-free and overall survival with combined therapy. Results were especially pronounced for patients with non-squamous lung cancer histologies, and in particular molecularly defined subgroups including KRAS mutations. These and other data from ARQ 197 clinical trials in hepatocellular, germ-cell, pancreatic (in combination with gemcitabine), and colorectal (in combination with cetuximab and irinotecan) cancers further highlight the potential role of ARQ 197 in existing and emerging anticancer therapeutic regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
The content of this article has been reviewed by independent peer reviewers to ensure that it is balanced, objective, and free from commercial bias. No financial relationships relevant to the content of this article have been disclosed by the independent peer reviewers.
Figures
References
-
- Furge KA, Zhang YW, Vande Woude GF. Met receptor tyrosine kinase: enhanced signaling through adapter proteins. Oncogene. 2000;19:5582–5589. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Gherardi E. Developmental roles of HGF/SF and its receptor, the c-Met tyrosine kinase. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, et al. Metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YW, Vande Woude GF. HGF/SF-met signaling in the control of branching morphogenesis and invasion. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88:408–417. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Hiscox S, Matsumoto K, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, its molecular, cellular and clinical implications in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1999;29:209–248. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

