Cortical deficits of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 expression in schizophrenia: clinical, protein, and cell type-specific features
- PMID: 21632647
- PMCID: PMC3273780
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11010052
Cortical deficits of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 expression in schizophrenia: clinical, protein, and cell type-specific features
Abstract
Objective: Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia are associated with altered activity of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which has been attributed to lower expression of the 67 kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67), the major γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-synthesizing enzyme. However, little is known about the relationship of prefrontal GAD67 mRNA levels and illness severity, translation of the transcript into protein, and protein levels in axon terminals, the key site of GABA production and function.
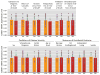
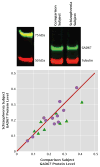
Method: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to measure GAD67 mRNA levels in postmortem specimens of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from subjects with schizophrenia and matched comparison subjects with no known history of psychiatric or neurological disorders (N=42 pairs). In a subset of this cohort in which potential confounds of protein measures were controlled (N=19 pairs), Western blotting was used to quantify tissue levels of GAD67 protein in tissue. In five of these pairs, multilabel confocal immunofluorescence was used to quantify GAD67 protein levels in the axon terminals of parvalbumin-containing GABA neurons, which are known to have low levels of GAD67 mRNA in schizophrenia.
Results: GAD67 mRNA levels were significantly lower in schizophrenia subjects (by 15%), but transcript levels were not associated with predictors or measures of illness severity or chronicity. In schizophrenia subjects, GAD67 protein levels were significantly lower in total gray matter (by 10%) and in parvalbumin axon terminals (by 49%).
Conclusions: The findings that lower GAD67 mRNA expression is common in schizophrenia, that it is not a consequence of having the illness, and that it leads to less translation of the protein, especially in the axon terminals of parvalbumin-containing neurons, support the hypothesis that lower GABA synthesis in parvalbumin neurons contributes to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex dysfunction and impaired cognition in schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Lewis receives investigator initiated research support from the BMS Foundation, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Curridium, and Pfizer and has served as a consultant in the areas of target identification and validation and new compound development to AstraZeneca, BioLine RX, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Neurogen, and SK Life Science. Dr. Sampson is a statistical consultant to Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development. All other authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Molecular etiologies of schizophrenia: are we almost there yet?Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Sep;168(9):879-81. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11050694. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21890799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

