Antifibrotic activities of pirfenidone in animal models
- PMID: 21632796
- PMCID: PMC9487788
- DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00001111
Antifibrotic activities of pirfenidone in animal models
Abstract
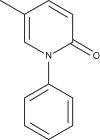
Pirfenidone is an orally active small molecule that has recently been evaluated in large clinical trials for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a fatal disease in which the uncontrolled deposition of extracellular matrix leads to progressive loss of lung function. This review describes the activity of pirfenidone in several well-characterised animal models of fibrosis in the lung, liver, heart and kidney. In these studies, treatment-related reductions in fibrosis are associated with modulation of cytokines and growth factors, with the most commonly reported effect being reduction of transforming growth factor-β. The consistent antifibrotic activity of pirfenidone in a broad array of animal models provides a strong preclinical rationale for the clinical characterisation of pirfenidone in pulmonary fibrosis and, potentially, other conditions with a significant fibrotic component.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employee shareholders of InterMune, Inc., which recently received European marketing authorisation for Esbriet® (pirfenidone) in the treatment of adult patients with mild to moderate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The article describes unpublished data from the laboratory of H. Oku, an employee of Shionogi and Co. Ltd, which markets pirfenidone for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Japan.
Figures

References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 277–304. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DT, Ding C, Wilson E, et al. . Pirfenidone mitigates left ventricular fibrosis and dysfunction after myocardial infarction and reduces arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm 2010; 7: 1438–1445. - PubMed
-
- Kelley CJ, Neilson EG. Tubulointerstitial diseases.. In: Brenner BM, ed. The Kidney. 5th Edn. Philadelphia, WB Saunders and Company, 1996; pp. 1655–1679.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
