Neutralising antibodies against ricin toxin
- PMID: 21633505
- PMCID: PMC3102095
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020166
Neutralising antibodies against ricin toxin
Abstract
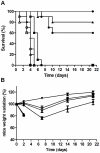
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have listed the potential bioweapon ricin as a Category B Agent. Ricin is a so-called A/B toxin produced by plants and is one of the deadliest molecules known. It is easy to prepare and no curative treatment is available. An immunotherapeutic approach could be of interest to attenuate or neutralise the effects of the toxin. We sought to characterise neutralising monoclonal antibodies against ricin and to develop an effective therapy. For this purpose, mouse monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were produced against the two chains of ricin toxin (RTA and RTB). Seven mAbs were selected for their capacity to neutralise the cytotoxic effects of ricin in vitro. Three of these, two anti-RTB (RB34 and RB37) and one anti-RTA (RA36), when used in combination improved neutralising capacity in vitro with an IC(50) of 31 ng/ml. Passive administration of association of these three mixed mAbs (4.7 µg) protected mice from intranasal challenges with ricin (5 LD(50)). Among those three antibodies, anti-RTB antibodies protected mice more efficiently than the anti-RTA antibody. The combination of the three antibodies protected mice up to 7.5 hours after ricin challenge. The strong in vivo neutralising capacity of this three mAbs combination makes it potentially useful for immunotherapeutic purposes in the case of ricin poisoning or possibly for prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
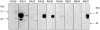
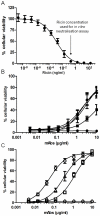
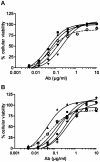
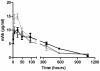



References
-
- Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin poisoning: a comprehensive review. JAMA. 2005;294:2342–2351. - PubMed
-
- Bigalke H, Rummel A. Medical aspects of toxin weapons. Toxicology. 2005;214:210–220. - PubMed
-
- Binder P, Attre O, Boutin JP, Cavallo JD, Debord T, et al. Medical management of biological warfare and bioterrorism: place of the immunoprevention and the immunotherapy. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003;26:401–421. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland DW, Fischer SG, Kirschner MW, Laemmli UK. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:1102–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

