Upregulation of adenosine kinase in astrocytes in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 21635241
- PMCID: PMC3169746
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03115.x
Upregulation of adenosine kinase in astrocytes in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Purpose: Adenosine kinase (ADK) represents the key metabolic enzyme for the regulation of extracellular adenosine levels in the brain. In adult brain, ADK is primarily present in astrocytes. Several lines of experimental evidence support a critical role of ADK in different types of brain injury associated with astrogliosis, which is also a prominent morphologic feature of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). We hypothesized that dysregulation of ADK is an ubiquitous pathologic hallmark of TLE.
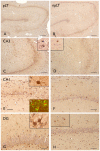
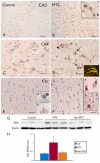
Methods: Using immunocytochemistry and Western blot analysis, we investigated ADK protein expression in a rat model of TLE during epileptogenesis and the chronic epileptic phase and compared those findings with tissue resected from TLE patients with mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS).
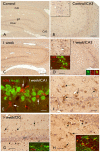
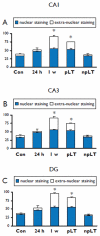
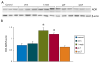
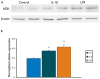
Key findings: In rat control hippocampus and cortex, a low baseline expression of ADK was found with mainly nuclear localization. One week after the electrical induction of status epilepticus (SE), prominent up-regulation of ADK became evident in astrocytes with a characteristic cytoplasmic localization. This increase in ADK persisted at least for 3-4 months after SE in rats developing a progressive form of epilepsy. In line with the findings from the rat model, expression of astrocytic ADK was also found to be increased in the hippocampus and temporal cortex of patients with TLE. In addition, in vitro experiments in human astrocyte cultures showed that ADK expression was increased by several proinflammatory molecules (interleukin-1β and lipopolysaccharide).
Significance: These results suggest that dysregulation of ADK in astrocytes is a common pathologic hallmark of TLE. Moreover, in vitro data suggest the existence of an additional layer of modulatory crosstalk between the astrocyte-based adenosine cycle and inflammation. Whether this interaction also can play a role in vivo needs to be further investigated.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2011 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ijlst-Keizers H, Rozemuller AJ, Yankaya B, Leenstra S, Troost D. Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:2106–2118. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Rozemuller AJ, Yankaya B, Troost D. Interleukin-1 beta down-regulates the expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in cultured human astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 2005;160:188–194. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Gorter J. Gene Expression Profile in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscientist. 2007;13:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Binder DK, Steinhauser C. Functional changes in astroglial cells in epilepsy. GLIA. 2006;54:358–368. - PubMed
-
- Blumcke I, Pauli E, Clusmann H, Schramm J, Becker A, Elger C, Merschhemke M, Meencke HJ, Lehmann T, von Deimling A, Scheiwe C, Zentner J, Volk B, Romstock J, Stefan H, Hildebrandt M. A new clinico-pathological classification system for mesial temporal sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:235–244. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

