Comparative studies of de novo assembly tools for next-generation sequencing technologies
- PMID: 21636596
- PMCID: PMC3137213
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr319
Comparative studies of de novo assembly tools for next-generation sequencing technologies
Abstract
Motivation: Several new de novo assembly tools have been developed recently to assemble short sequencing reads generated by next-generation sequencing platforms. However, the performance of these tools under various conditions has not been fully investigated, and sufficient information is not currently available for informed decisions to be made regarding the tool that would be most likely to produce the best performance under a specific set of conditions.
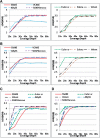
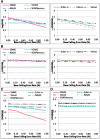
Results: We studied and compared the performance of commonly used de novo assembly tools specifically designed for next-generation sequencing data, including SSAKE, VCAKE, Euler-sr, Edena, Velvet, ABySS and SOAPdenovo. Tools were compared using several performance criteria, including N50 length, sequence coverage and assembly accuracy. Various properties of read data, including single-end/paired-end, sequence GC content, depth of coverage and base calling error rates, were investigated for their effects on the performance of different assembly tools. We also compared the computation time and memory usage of these seven tools. Based on the results of our comparison, the relative performance of individual tools are summarized and tentative guidelines for optimal selection of different assembly tools, under different conditions, are provided.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

