Pathway inhibition: emerging molecular targets for treating glioblastoma
- PMID: 21636705
- PMCID: PMC3107100
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor039
Pathway inhibition: emerging molecular targets for treating glioblastoma
Abstract
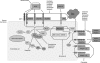
Insights into the molecular pathogenesis of glioblastoma have not yet resulted in relevant clinical improvement. With standard therapy, which consists of surgical resection with concomitant temozolomide in addition to radiotherapy followed by adjuvant temozolomide, the median duration of survival is 12-14 months. Therefore, the identification of novel molecular targets and inhibitory agents has become a focus of research for glioblastoma treatment. Recent results of bevacizumab may represent a proof of principle that treatment with targeted agents can result in clinical benefits for patients with glioblastoma. This review discusses limitations in the existing therapy for glioblastoma and provides an overview of current efforts to identify molecular targets using large-scale screening of glioblastoma cell lines and tumor samples. We discuss preclinical and clinical data for several novel molecular targets, including growth factor receptors, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, SRC-family kinases, integrins, and CD95 ligand and agents that inhibit these targets, including erlotinib, enzastaurin, dasatinib, sorafenib, cilengitide, AMG102, and APG101. By combining advances in tumor screening with novel targeted therapies, it is hoped that new treatment options will emerge for this challenging tumor type.
Figures
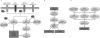
References
-
- Hess KR, Broglio KR, Bondy ML. Adult glioma incidence trends in the United States, 1977–2000. Cancer. 2004;101:2293–2299. doi:10.1002/cncr.20621. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0708126. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wick A, Pascher C, Wick W, et al. Rechallenge with temozolomide in patients with recurrent gliomas. J Neurol. 2009;256:734–741. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-5006-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Perry JR, Belanger K, Mason WP, et al. Phase II trial of continuous dose-intense temozolomide in recurrent malignant glioma: RESCUE study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2051–2057. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.5520. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

