The Dynamical Systems Properties of the HOG Signaling Cascade
- PMID: 21637384
- PMCID: PMC3100117
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/930940
The Dynamical Systems Properties of the HOG Signaling Cascade
Abstract
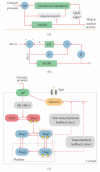
The High Osmolarity Glycerol (HOG) MAP kinase pathway in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is one of the best characterized model signaling pathways. The pathway processes external signals of increased osmolarity into appropriate physiological responses within the yeast cell. Recent advances in microfluidic technology coupled with quantitative modeling, and techniques from reverse systems engineering have allowed yet further insight into this already well-understood pathway. These new techniques are essential for understanding the dynamical processes at play when cells process external stimuli into biological responses. They are widely applicable to other signaling pathways of interest. Here, we review the recent advances brought by these approaches in the context of understanding the dynamics of the HOG pathway signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coordination of the Cell Wall Integrity and High-Osmolarity Glycerol Pathways in Response to Ethanol Stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jul 18;85(15):e00551-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00551-19. Print 2019 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31101611 Free PMC article.
-
Response to high osmotic conditions and elevated temperature in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by intracellular glycerol and involves coordinate activity of MAP kinase pathways.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 May;149(Pt 5):1193-1204. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26110-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12724381
-
Yeast osmoregulation.Methods Enzymol. 2007;428:29-45. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)28002-4. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17875410 Review.
-
Regulation of the osmoregulatory HOG MAPK cascade in yeast.J Biochem. 2004 Sep;136(3):267-72. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh135. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15598881 Review.
-
Osmotic adaptation in yeast--control of the yeast osmolyte system.Int Rev Cytol. 2002;215:149-87. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(02)15008-x. Int Rev Cytol. 2002. PMID: 11952227 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperosmotic Stress Response Memory is Modulated by Gene Positioning in Yeast.Cells. 2019 Jun 13;8(6):582. doi: 10.3390/cells8060582. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31200564 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Posttranslational Control in Cellular Stress Response Pathways and Its Relationship to Toxicity Testing and Safety Assessment.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Oct;147(2):302-16. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv130. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26408567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated pathway system modeling of Saccharomyces cerevisiae HOG pathway: a Petri net based approach.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Feb;40(2):1103-25. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2153-3. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23086300
-
Long-term model predictive control of gene expression at the population and single-cell levels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 28;109(35):14271-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206810109. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22893687 Free PMC article.
-
The Phosphatome of Medicinal and Edible Fungus Wolfiporia cocos.Curr Microbiol. 2018 Feb;75(2):124-131. doi: 10.1007/s00284-017-1356-1. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Curr Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28900701
References
-
- Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW. From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature. 1999;402(6761):C47–C52. - PubMed
-
- Nurse P. Life, logic and information. Nature. 2008;454(7203):424–426. - PubMed
-
- Brent R. Cell signaling: what is the signal and what information does it carry? FEBS Letters. 2009;583(24):4019–4024. - PubMed
-
- Novère NL, Hucka M, Mi H, et al. The systems biology graphical notation. Nature Biotechnology. 2009;27(8):735–741. - PubMed
-
- Jovic A, Howell B, Takayama S. Timing is everything: using fluidics to understand the role of temporal dynamics in cellular systems. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. 2009;6(6):717–729.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

