Association of genetic variants in complement factor H and factor H-related genes with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility
- PMID: 21637784
- PMCID: PMC3102741
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002079
Association of genetic variants in complement factor H and factor H-related genes with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility
Abstract
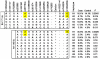
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a complex polygenic autoimmune disease, is associated with increased complement activation. Variants of genes encoding complement regulator factor H (CFH) and five CFH-related proteins (CFHR1-CFHR5) within the chromosome 1q32 locus linked to SLE, have been associated with multiple human diseases and may contribute to dysregulated complement activation predisposing to SLE. We assessed 60 SNPs covering the CFH-CFHRs region for association with SLE in 15,864 case-control subjects derived from four ethnic groups. Significant allelic associations with SLE were detected in European Americans (EA) and African Americans (AA), which could be attributed to an intronic CFH SNP (rs6677604, in intron 11, P(meta) = 6.6×10(-8), OR = 1.18) and an intergenic SNP between CFHR1 and CFHR4 (rs16840639, P(meta) = 2.9×10(-7), OR = 1.17) rather than to previously identified disease-associated CFH exonic SNPs, including I62V, Y402H, A474A, and D936E. In addition, allelic association of rs6677604 with SLE was subsequently confirmed in Asians (AS). Haplotype analysis revealed that the underlying causal variant, tagged by rs6677604 and rs16840639, was localized to a ~146 kb block extending from intron 9 of CFH to downstream of CFHR1. Within this block, the deletion of CFHR3 and CFHR1 (CFHR3-1Δ), a likely causal variant measured using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification, was tagged by rs6677604 in EA and AS and rs16840639 in AA, respectively. Deduced from genotypic associations of tag SNPs in EA, AA, and AS, homozygous deletion of CFHR3-1Δ (P(meta) = 3.2×10(-7), OR = 1.47) conferred a higher risk of SLE than heterozygous deletion (P(meta) = 3.5×10(-4), OR = 1.14). These results suggested that the CFHR3-1Δ deletion within the SLE-associated block, but not the previously described exonic SNPs of CFH, might contribute to the development of SLE in EA, AA, and AS, providing new insights into the role of complement regulators in the pathogenesis of SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929–939. - PubMed
-
- Manderson AP, Botto M, Walport MJ. The role of complement in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:431–456. - PubMed
-
- Miyagawa H, Yamai M, Sakaguchi D, Kiyohara C, Tsukamoto H, et al. Association of polymorphisms in complement component C3 gene with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:158–164. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes B, Hunnangkul S, Morris DL, Hsaio LC, Graham DS, et al. The heritability and genetics of complement C3 expression in UK SLE families. Genes Immun. 2009;10:525–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01AR49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60AR049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P602AR30692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR030692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- I ULI RR025014-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G0701325/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RC1AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 RR031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- LRPAI071651/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR051545-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR33062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR054459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1AR058554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051545/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI050026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

