Infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis: alone or in combination with methotrexate? A pharmacokinetic comparative study
- PMID: 21639907
- PMCID: PMC3218893
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3350
Infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis: alone or in combination with methotrexate? A pharmacokinetic comparative study
Abstract
Introduction: Methotrexate (MTX) has been shown to modify infliximab pharmacokinetics in rheumatoid arthritis. However, its combination with infliximab in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is not recommended. The objective of this study was to examine the influence of MTX on infliximab exposure in patients with AS.
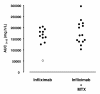
Methods: Patients with AS patients who had predominantly axial symptoms were randomised to receive infliximab alone (infusions of 5 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, 6, 12 and 18) or infliximab combined with MTX (10 mg/week). Infliximab concentrations were measured before and 2 hours after each infusion and at 1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 14 and 18 weeks. We estimated individual cumulative area under the concentration versus time curves (AUC) for infliximab concentration between baseline and week 18 (AUC(0-18)). Clinical and laboratory evaluations were performed at each visit. The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score was the primary end point for clinical response.
Results: Twenty-six patients were included (infliximab group: n = 12, infliximab + MTX group: n = 14), and 507 serum samples were available for measurement of infliximab concentration. The two groups did not differ with regard to AUC(0-18) or evolution of BASDAI scores and biomarkers of inflammation.
Conclusions: The combination of MTX and infliximab does not increase the exposure to infliximab over infliximab alone in patients with AS.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00507403.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez-Lopez L, Garcia-Gonzalez A, Vazquez-Del-Mercado M, Muñoz-Valle JF, Gamez-Nava JI. Efficacy of methotrexate in ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1568–1574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

