Decreased cell adhesion promotes angiogenesis in a Pyk2-dependent manner
- PMID: 21640103
- PMCID: PMC3123418
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.006
Decreased cell adhesion promotes angiogenesis in a Pyk2-dependent manner
Abstract
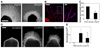
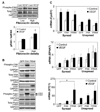
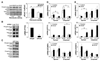
Angiogenesis is regulated by both soluble growth factors and cellular interactions with the extracellular matrix (ECM). While cell adhesion via integrins has been shown to be required for angiogenesis, the effects of quantitative changes in cell adhesion and spreading against the ECM remain less clear. Here, we show that angiogenic sprouting in natural and engineered three-dimensional matrices exhibited a biphasic response, with peak sprouting when adhesion to the matrix was limited to intermediate levels. Examining changes in global gene expression to determine a genetic basis for this response, we demonstrate a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced upregulation of genes associated with vascular invasion and remodeling when cell adhesion was limited, whereas cells on highly adhesive surfaces upregulated genes associated with proliferation. To explore a mechanistic basis for this effect, we turned to focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a central player in adhesion signaling previously implicated in angiogenesis, and its homologue, proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2). While FAK signaling had some impact, our results suggested that Pyk2 can regulate both gene expression and endothelial sprouting through its enhanced activation by VEGF in limited adhesion contexts. We also demonstrate decreased sprouting of tissue explants from Pyk2-null mice as compared to wild type mice as further confirmation of the role of Pyk2 in angiogenic sprouting. These results suggest a surprising finding that limited cell adhesion can enhance endothelial responsiveness to VEGF and demonstrate a novel role for Pyk2 in the adhesive regulation of angiogenesis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996;380:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell- Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature. 1996;380:439–442. - PubMed
-
- Miquerol L, Langille BL, Nagy A. Embryonic development is disrupted by modest increases in vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression. Development. 2000;127:3941–3946. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

