Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase inhibition in blood ameliorates neurodegeneration
- PMID: 21640374
- PMCID: PMC3118409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.020
Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase inhibition in blood ameliorates neurodegeneration
Abstract
Metabolites in the kynurenine pathway, generated by tryptophan degradation, are thought to play an important role in neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases. In these disorders, glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxicity and free radical formation have been correlated with decreased levels of the neuroprotective metabolite kynurenic acid. Here, we describe the synthesis and characterization of JM6, a small-molecule prodrug inhibitor of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO). Chronic oral administration of JM6 inhibits KMO in the blood, increasing kynurenic acid levels and reducing extracellular glutamate in the brain. In a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, JM6 prevents spatial memory deficits, anxiety-related behavior, and synaptic loss. JM6 also extends life span, prevents synaptic loss, and decreases microglial activation in a mouse model of Huntington's disease. These findings support a critical link between tryptophan metabolism in the blood and neurodegeneration, and they provide a foundation for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
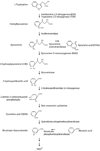
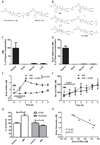
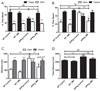
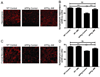


Comment in
-
Treating the periphery to ameliorate neurodegenerative diseases.Cell. 2011 Jun 10;145(6):813-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.031. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21663784
-
Neurodegenerative disease: the kynurenine pathway--promising new targets and therapies for neurodegenerative disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2011 Jul 26;7(8):417. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.102. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21788979 No abstract available.
-
Neurodegenerative disorders: restoring the balance.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Aug 1;10(8):576. doi: 10.1038/nrd3521. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21804592 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andiné P, Lehmann A, Ellren K, Wennberg E, Kjellmer I, Nielsen T, Hagberg H. The excitatory amino acid antagonist kynurenic acid administered after hypoxic-ischemia in neonatal rats offers neuroprotection. Neurosci Lett. 1988;90:208–212. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Matson WR, Storey E, Milbury P, Ryan EA, Ogawa T, Bird ED. Kynurenic acid concentrations are reduced in Huntington’s disease cerebral cortex. J Neurol Sci. 1992;108:80–87. - PubMed
-
- Boegman RJ, el-Defrawy SR, Jhamandas K, Beninger RJ, Ludwin SK. Quinolinic acid neurotoxicity in the nucleus basalis antagonized by kynurenic acid. Neurobiol Aging. 1985;6:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

