Delta-aminolevulinic dehydratase is a proteasome interacting protein
- PMID: 21640720
- PMCID: PMC3185203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.05.003
Delta-aminolevulinic dehydratase is a proteasome interacting protein
Abstract
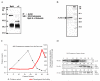
The proteasome interacts with a large number of proteins which regulate specific cellular functions. The focus of this study is to examine the proteasome interaction with Delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase (ALAD). ALAD is involved in the heme biosynthesis pathway and was co-isolated, with the 20S proteasome using several chromatographic purification steps. The MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis identified this proteasome co-isolated protein as ALAD. When the proteasome was isolated using density-gradient centrifugation, ALAD was also found in the 26S proteasome fractions. It co-isolated with the 20S more than with the 26S proteasome. Furthermore, immunoprecipitated ALAD stained positive with antibodies to proteasome subunits. These results indicate that ALAD might interact with the proteasome. It is possible that ALAD is involved in modulating proteasome activity. When purified proteasomes were incubated with ALAD it was found that ALAD changes proteasome activity in a dose dependent manner. This indicates that ALAD may play a significant role in regulating proteasome activity. The data supports the hypothesis that ALAD, an important enzyme for heme synthesis, is also important as a proteasome interacting protein.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bardag-Gorce F, Venkatesh R, Li J, French BA, French SW. Hyperphosphorylation of rat liver proteasome subunits: the effects of ethanol and okadaic acid are compared. Life Sci. 2004;75(5):585–597. - PubMed
-
- Bercovich B, Stancovski I, Mayer A, Blumenfeld N, Laszlo A, Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A. Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of certain protein substrates in vitro requires the molecular chaperone Hsc70. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272(14):9002–9010. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;7:72, 248–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

