Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase
- PMID: 21641547
- PMCID: PMC3257518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.023
Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase
Abstract
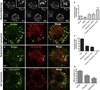
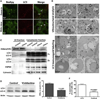
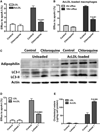
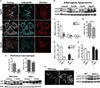
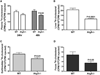
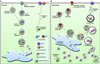
The lipid droplet (LD) is the major site of cholesterol storage in macrophage foam cells and is a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Cholesterol, stored as cholesteryl esters (CEs), is liberated from this organelle and delivered to cholesterol acceptors. The current paradigm attributes all cytoplasmic CE hydrolysis to the action of neutral CE hydrolases. Here, we demonstrate an important role for lysosomes in LD CE hydrolysis in cholesterol-loaded macrophages, in addition to that mediated by neutral hydrolases. Furthermore, we demonstrate that LDs are delivered to lysosomes via autophagy, where lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) acts to hydrolyze LD CE to generate free cholesterol mainly for ABCA1-dependent efflux; this process is specifically induced upon macrophage cholesterol loading. We conclude that, in macrophage foam cells, lysosomal hydrolysis contributes to the mobilization of LD-associated cholesterol for reverse cholesterol transport.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Avart SJ, Bernard DW, Jerome WG, Glick JM. Cholesteryl ester hydrolysis in J774 macrophages occurs in the cytoplasm and lysosomes. J. Lipid Res. 1999;40:405–414. - PubMed
-
- Azuma Y, Takada M, Shin HW, Kioka N, Nakayama K, Ueda K. Retroendocytosis pathway of ABCA1/apoA-I contributes to HDL formation. Genes Cells. 2009;14:191–204. - PubMed
-
- Basso MD, Nambi P, Adelman SJ. Effect of sirolimus on the cholesterol content of aortic arch in ApoE knockout mice. Transplant. Proc. 2003;35:3136–3138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

