FGF15/19 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by inhibiting the CREB-PGC-1α pathway
- PMID: 21641554
- PMCID: PMC3131185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.019
FGF15/19 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by inhibiting the CREB-PGC-1α pathway
Abstract
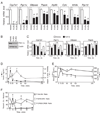
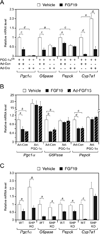
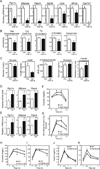
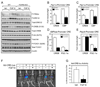
Regulation of hepatic carbohydrate homeostasis is crucial for maintaining energy balance in the face of fluctuating nutrient availability. Here, we show that the hormone fibroblast growth factor 15/19 (FGF15/19), which is released postprandially from the small intestine, inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis, like insulin. However, unlike insulin, which peaks in serum 15 min after feeding, FGF15/19 expression peaks approximately 45 min later, when bile acid concentrations increase in the small intestine. FGF15/19 blocks the expression of genes involved in gluconeogenesis through a mechanism involving the dephosphorylation and inactivation of the transcription factor cAMP regulatory element-binding protein (CREB). This in turn blunts expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) and other genes involved in hepatic metabolism. Overexpression of PGC-1α blocks the inhibitory effect of FGF15/19 on gluconeogenic gene expression. These results demonstrate that FGF15/19 works subsequent to insulin as a postprandial regulator of hepatic carbohydrate homeostasis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ahren B, Havel PJ. Leptin increases circulating glucose, insulin and glucagon via sympathetic neural activation in fasted mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23:660–665. - PubMed
-
- Ayala JE, Bracy DP, McGuinness OP, Wasserman DH. Considerations in the design of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps in the conscious mouse. Diabetes. 2006;55:390–397. - PubMed
-
- Bittinger MA, McWhinnie E, Meltzer J, Iourgenko V, Latario B, Liu X, Chen CH, Song C, Garza D, Labow M. Activation of cAMP response element-mediated gene expression by regulated nuclear transport of TORC proteins. Curr Biol. 2004;14:2156–2161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

