Combining PubMed knowledge and EHR data to develop a weighted bayesian network for pancreatic cancer prediction
- PMID: 21642013
- PMCID: PMC3174321
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2011.05.004
Combining PubMed knowledge and EHR data to develop a weighted bayesian network for pancreatic cancer prediction
Abstract
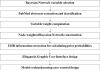
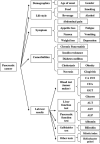
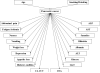
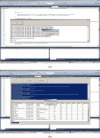
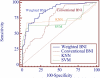
In this paper, we propose a novel method that combines PubMed knowledge and Electronic Health Records to develop a weighted Bayesian Network Inference (BNI) model for pancreatic cancer prediction. We selected 20 common risk factors associated with pancreatic cancer and used PubMed knowledge to weigh the risk factors. A keyword-based algorithm was developed to extract and classify PubMed abstracts into three categories that represented positive, negative, or neutral associations between each risk factor and pancreatic cancer. Then we designed a weighted BNI model by adding the normalized weights into a conventional BNI model. We used this model to extract the EHR values for patients with or without pancreatic cancer, which then enabled us to calculate the prior probabilities for the 20 risk factors in the BNI. The software iDiagnosis was designed to use this weighted BNI model for predicting pancreatic cancer. In an evaluation using a case-control dataset, the weighted BNI model significantly outperformed the conventional BNI and two other classifiers (k-Nearest Neighbor and Support Vector Machine). We conclude that the weighted BNI using PubMed knowledge and EHR data shows remarkable accuracy improvement over existing representative methods for pancreatic cancer prediction.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of patients at risk for pancreatic cancer in a 3-year timeframe based on machine learning algorithms.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 5;15(1):11697. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89607-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40188106 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype risk scores (PheRS) for pancreatic cancer using time-stamped electronic health record data: Discovery and validation in two large biobanks.J Biomed Inform. 2021 Jan;113:103652. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103652. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Biomed Inform. 2021. PMID: 33279681 Free PMC article.
-
Cost sensitive hierarchical document classification to triage PubMed abstracts for manual curation.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Dec 19;12:482. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-482. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 22182279 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized Pancreatic Cancer Management: A Systematic Review of How Machine Learning Is Supporting Decision-making.Pancreas. 2019 May/Jun;48(5):598-604. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001312. Pancreas. 2019. PMID: 31090660
-
Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Applying Artificial Intelligence to Electronic Health Records.Pancreas. 2021 Aug 1;50(7):916-922. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001882. Pancreas. 2021. PMID: 34629446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Making sense of health care delivery Where does the close to community health care worker fit in? - The case for congestive heart failure.Indian Heart J. 2015 May-Jun;67(3):250-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2015.03.013. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Indian Heart J. 2015. PMID: 26138183 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the risk of cancer in adults using supervised machine learning: a scoping review.BMJ Open. 2021 Sep 14;11(9):e047755. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047755. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34521662 Free PMC article.
-
Learning to predict post-hospitalization VTE risk from EHR data.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2012;2012:436-45. Epub 2012 Nov 3. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2012. PMID: 23304314 Free PMC article.
-
Probabilistic Prognostic Estimates of Survival in Metastatic Cancer Patients (PPES-Met) Utilizing Free-Text Clinical Narratives.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 3;8(1):10037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27946-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29968730 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Prediction Model to Estimate Individual Risk of Pancreatic Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 11;11(1):e0146473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146473. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26752291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim DJ, Rockhill B, Colditz GA. Validation of the Harvard Cancer Risk Index: a prediction tool for individual cancer risk. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57(4):332–340. - PubMed
-
- Heckerman D. A tutorial on learning with Bayesian Networks. Microsoft Research Tech Report. 1995:57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

