Identifying vulnerable pathways in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by using a knockdown approach
- PMID: 21642404
- PMCID: PMC3147394
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02880-10
Identifying vulnerable pathways in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by using a knockdown approach
Abstract
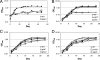
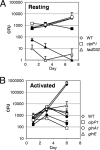
We constructed recombinant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in which expression of specific genes was downregulated to identify vulnerable drug targets. Growth phenotypes in macrophages and culture were used to rank targets: the dprE1, clpP1, and fadD32 operons were the best targets and glnA1, glnE, pknL, regX3, and senX3 were poor targets.
Figures

References
-
- Anishetty S., Pulimi M., Pennathur G. 2005. Potential drug targets in Mycobacterium tuberculosis through metabolic pathway analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 29:368–378 - PubMed
-
- Boshoff H. I., et al. 2004. The transcriptional responses of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to inhibitors of metabolism: novel insights into drug mechanisms of action. J. Biol. Chem. 279:40174–40184 - PubMed
-
- Goude R., Parish T. 2009. Electroporation of mycobacteria. Methods Mol. Biol. 465:203–215 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

