Exceptional production of both prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin as major metabolic constituents by a novel marine bacterium, Zooshikella rubidus S1-1
- PMID: 21642414
- PMCID: PMC3147376
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01986-10
Exceptional production of both prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin as major metabolic constituents by a novel marine bacterium, Zooshikella rubidus S1-1
Abstract
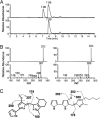
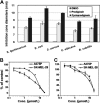
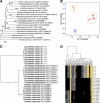
A Gram-negative, red-pigment-producing marine bacterial strain, designated S1-1, was isolated from the tidal flat sediment of the Yellow Sea, Korea. On the basis of phenotypic, phylogenetic, and genetic data, strain S1-1 (KCTC 11448BP) represented a new species of the genus Zooshikella. Thus, we propose the name Zooshikella rubidus sp. nov. Liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry of the red pigments produced by strain S1-1 revealed that the major metabolic compounds were prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin. In addition, this organism produced six minor prodigiosin analogues, including two new structures that were previously unknown. To our knowledge, this is the first description of a microorganism that simultaneously produces prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin as two major metabolites. Both prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin showed antimicrobial activity against several microbial species. These bacteria were approximately 1.5-fold more sensitive to cycloprodigiosin than to prodigiosin. The metabolites also showed anticancer activity against human melanoma cells, which showed significantly more sensitivity to prodigiosin than to cycloprodigiosin. The secondary metabolite profiles of strain S1-1 and two reference bacterial strains were compared by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Multivariate statistical analyses based on secondary metabolite profiles by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry indicated that the metabolite profile of strain S1-1 could clearly be distinguished from those of two phylogenetically related, prodigiosin-producing bacterial strains.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett J. W., Bentley R. 2000. Seeing red: the story of prodigiosin. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 47:1–32 - PubMed
-
- Boger D. L., Patel M. 1988. Total synthesis of prodigiosin, prodigiosene, and desmethoxyprodigiosin: Diels-Alder reactions of heterocyclic azadienes and development of an effective palladium(II)-promoted 2,2′-bipyrrole coupling procedure. J. Org. Chem. 53:1405–1415
-
- Castro A. J. 1967. Antimalarial activity of prodigiosin. Nature 213:903–904 - PubMed
-
- Cerdeño A. M., Bibb M. J., Challis G. L. 2001. Analysis of the prodiginine biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): new mechanisms for chain initiation and termination in modular multienzymes. Chem. Biol. 8:817–829 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

